THE COMPLETE HIGH SCHOOL STUDY GUIDE – EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO ACE BIOLOGY IN ONE BIG FAT NOTEBOOK
UNIT 1: Basics of Biology
Chapter 1: Introdution to Biology
WAHT IS BIOLOGY
living things -> organism
organism
- 有机体系
a system consisting of parts that depend on each other - a living thing, especially one that is extremely small
life cycle
- organisms grow, change, reproduce, and die.
the series of changes that organism can go through are called the life cycle. - a human life cycle: infancy -> childhood -> adolescence -> adulthood -> fertilization
infancy
婴儿期;
the time when a child is a baby or very youngadolescence
青春期;
the time in a person’s life when he or she develops from a child into an adult
World Health Organization definition officially designates an adolescent as someone between the ages of 10 and 19.puberty
青春期
the period of a person’s life during which their sexual organs develop and they become capable of having children
It is a process that usually happens between ages 10 and 14 for girls and ages 12 and 16 for boys.fertilization
(胚)受精
creation by the physical union of male and female gametes
(农)施肥
making fertile as by applying fertilizer or manurefertilizer
肥料
Fertilizer is a substance such as solid animal waste or a chemical mixture that you spread on the ground in order to make plants grow more successfully.粪肥
the waste matter from animals that is spread over or mixed with the soil to help plants and crops grow
TYPE OF BIOLOGY: disciplines
| BRANCH | THE STUDY OF… |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | the bodily structure of organisms. |
| Botany | plants. |
| Ecology | the relationships between various organisms. |
| Microbiology | tiny organisms. |
| Pathology | the causes and effects of diseases. |
| Pharmacology | the uses and effects of drugs. |
| Physiology | the functions of living organisms and their parts. |
| Taxonomy | the classification of organisms. |
| Toxicology | the nature and effects of poisons. |
| Zoology | animals |
Anatomy
解剖学
the scientific study of the structure of human or animal bodies
Botany
植物学
the scientific study of plants and their structure
Zoology
动物学
the scientific study of animals and their behaviour
Pathology
病理学
Pharmacology
药理学
the scientific study of drugs and their use in medicine
Physiology
生理学
生理学是生物学的一个主要分支,是研究生物机体的各种生命现象,特别是机体各组成部分的功能及实现其功能的内在机制的一门学科。
Taxonomy
分类学
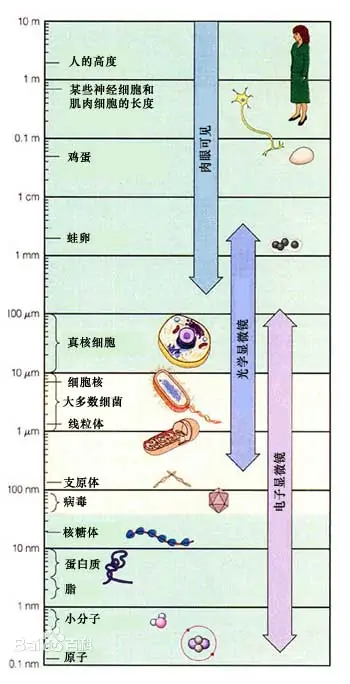
THE TOOLS OF THE BILOGIST
- Microscopes
the most basic concept in biology – organisms are made uo of cells
e basic function: to show details in
objects that cannot be seen by the naked human eye.
compound(light) microscope.
It has two lenses: the OCULAR LENS that we look through and the two OBJECTIVE LENSES that are closer to the SLIDE .
SLIDE: A thin piece of glass used to hold a specimen
SPECIMEN: A sample that is studied. a small amount of sth that shows what the rest of it is like
光学显微镜
通常皆由光学部分、照明部分和机械部分组成。无疑光学部分是最为关键的,它由目镜和物镜组成。
电子显微镜有与光学显微镜相似的基本结构特征,但它有着比光学显微镜高得多的对物体的放大及分辨本领,它将电子流作为一种新的光源,使物体成像。
透射电子显微镜
因电子束穿透样品后,再用电子透镜成像放大而得名。它的光路与光学显微镜相仿,可以直接获得一个样本的投影。通过改变物镜的透镜系统人们可以直接放大物镜的焦点的像。
电子透镜用来聚焦电子,是电子显微镜镜筒中最重要的部件。
它用一个对称于镜筒轴线的空间电场或磁场使电子轨迹向轴线弯曲形成聚焦,其作用与光学显微镜中的光学透镜(凸透镜)使光束聚焦的作用是一样的,所以称为电子透镜。光学透镜的焦点是固定的,而电子透镜的焦点可以被调节
- X-RAY
X-rays are a type of RADIATION that are
absorbed by various things.
RADIATION
The transmission of energy in the form of waves through an object.
When a human, or animal, undergoes an X-ray, the image taken of their body reveals the structures that absorbed the most radiation.
In the picture, bones appear white because the calcium in them absorbs the most radiation.
Everything else in the body absorbs less radiation, causing the color of the organs to look gray or black.
- MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SCANS (MRIs)
MRIs use a magnet and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal organs and muscles that might not show up in an X-ray.
(medical 医) 磁共振成像a method of using a strong magnetic field to produce an image of the inside of a person’s body
resonance共振;谐振
the sound or other vibration produced in an object by sound or vibrations of a similar frequency from another object
Chapter 2: CRITICAL THINKING IN BIOLOGY
Chapter 3: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE
- They are made of one or more CELLS, The basic units of life.
- They need energy to live.
- They respond to STIMULI((使生物产生反应的)刺激Anything that causes a response)–they react to their enviroment(for instance,light,temperature,and touch)
LIFE FUNCTIONS
All ORGANISMS (living things) must have the potential to carry out certain behaviors, known as LIFE FUNCTIONS .
Life functions are processes that an organism takes on to help it survive. The life functions are:
Growth: an increase in the number of cells
As more cells are made, the organism goes through the process of growth.
The growth in cells helps them live better in their environment.Reproduction: the creation of a new organism with its own cells.
The new organism is referred to as OFFSPRING(后代).
Some offspring are born looking like their parents (for example, human babies);
other offspring are born in one form and then change as they grow to another (like tadpoles蝌蚪 changing into frogs).Reproduction can happen with either one- or two-parent organisms.
- When one parent organism reproduces by itself, the process is called ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION. The offspring looks like the parent. Bacteria usually reproduce asexually.
- When two parents reproduce, it ’s called SEXUAL REPRODUCTION. Many plants and animals are sexual reproducers.
Nutrition营养的补给: the taking in of food(nutrients: Any substance that promotes life and provides energy. All living things need NUTRIENTS to survive. Nutrients keep an organism healthy.)
Organisms can be categorized according to how they get their nutrition:
- AUTOTROPHS , organisms that can make their own food, such as plants.
- HETEROTROPHS , organisms that cannot make their own food, such as animals.
Auto comes from the Greek word autos, meaning “self.”
hetero
- prefix: hetero-
异质的;不同的;
other; different. - heterosexual: sexually or romantically attracted exclusively to people of the other sex.
troph
The meaning of TROPH- is nutritive.respiration: the breakdown of nutrients to get energy
respiration
呼吸the act of breathing
the metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules
metabolic metabolism新陈代谢
the chemical processes in living things that change food, etc. into energy and materials for growth
UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
UNIT 3: Cell Theory
UNIT 4: Bacteria, Viruses, Prions, and Viroids
Bacteria细菌
bacterium的复数
the simplest and smallest forms of life. Bacteria exist in large numbers in air, water and soil, and also in living and dead creatures and plants, and are often a cause of disease.
Viruses
/ˈvaɪrəsəz/
病毒
Prions 朊病毒
Viroids
类病毒
UNIT 5: Protists
protist
原生生物
free-living or colonial organisms with diverse nutritional and reproductive modes
UNIT 6: Fungi
fungus
真菌(如蘑菇和霉)
any plant without leaves, flowers or green colouring, usually growing on other plants or on decaying matter. Mushrooms and mildew are both fungi .
UNIT 7: Plants
UNIT 8: Animals
UNIT 9: The Human Body
UNIT 10: Genetics
UNIT 11: Life on Earth
UNIT 12: Ecosytems and Habitats
habitat
栖息地
the place where a particular type of animal or plant is normally found
The habitat of an animal or plant is the natural environment in which it normally lives or grows.