Computer DIY
Motherboard 主板
Form factor
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics
ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration specification, patented by David Dent in 1995 at Intel
It was the first major change in desktop computer enclosure, motherboard and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts.
The specification defines the dimensions; the mounting points; the I/O panel; and the power and connector interfaces among a computer case, a motherboard, and a power supply.
ATX(Advanced Technology Extended)主板规格由英特尔公司在1995年制定。
ATX connectors
ATX allowed each motherboard manufacturer to put these ports in a rectangular area on the back of the system with an arrangement they could define themselves, though a number of general patterns depending on what ports the motherboard offers have been followed by most manufacturers.
Cases are usually fitted with a snap-out panel, also known as an I/O plate or I/O shield, in one of the common arrangements.
I/O plates are usually included with retail motherboards to allow installation in any suitable case.
The computer will operate correctly without a plate fitted, although there will be open gaps in the case which may compromise the EMI/RFI screening and allow ingress of dirt and random foreign bodies.
Some ATX motherboards come with an integrated I/O plate.
A notable issue with the ATX specification was that it was last revised when power supplies were normally placed at the top of many old computer cases rather than at the bottom, as with many modern computer cases. This has led to some problematic standard locations for ports, in particular the 4/8 pin CPU power.
Modern power supplies often have longer cables to alleviate this issue.
EATX
EATX (Extended ATX) is a bigger version of the ATX motherboard with 12 × 13 in (305 × 330 mm) dimensions.
the extra size of EATX makes it the typical form factor for dual socket systems, and with sockets that support four or eight memory channels, for single socket systems with a large number of memory slots.
E-ATX motherboards and cases are still in production (as of 2020), and support quad-channel memory across 8 slots of ram, up to 4 PCI-e expansion slots for up to 4 double slot graphics cards and a single CPU such as the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 3990X.
Although true E-ATX is 12 × 13 in (305 × 330 mm) most motherboard manufacturers also refer to motherboards with measurements 12 × 10.1 in (305 × 257 mm), 12 × 10.4 in (305 × 264 mm), 12 × 10.5 in (305 × 267 mm) and 12 × 10.7 in (305 × 272 mm) as E-ATX.
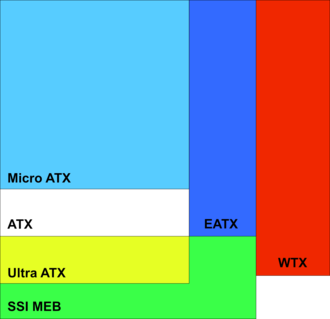
ATX motherboard size comparison; rear is on left.

microATX (244 × 244 mm)
Standard ATX (305 × 244 mm)
Ultra ATX (366 × 244 mm)
Extended ATX (EATX) (305 × 330 mm)
WTX (356 × 425 mm)
SSI MEB (411 × 330 mm)
SSI CEB
The Compact Electronics Bay Specification (CEB) as well as EEB, MEB and TEB (“Thin Electronics Bay”) are standard form factors for dual or multi processor motherboards defined by the Server System Infrastructure (SSI) Forum.
The specification is intended for value servers and workstations based on the Intel Xeon, and AMD Epyc processors (X399/C600 chipsets)
| Name | Form factor (Height × Length) |
|---|---|
| Compact Electronics Bay (CEB) | 12 × 10.5 in (305 × 267 mm) |
| Enterprise Electronics Bay (EEB) | 12 × 13 in (305 × 330 mm) |
| Midrange Electronics Bay (MEB) | 16.2 × 13 in (411 × 330 mm) |
Ultra ATX
Ultra ATX is an 14.4 × 9.6 in (366 × 244 mm) motherboard form factor proposed by Foxconn during CES in January 2008. In principle, it is simply an oversized version of ATX that supports 10 expansion slots, as opposed to the seven slots of ATX, and it requires a full-tower computer case to support the added height of the motherboard.
Video cards often trend towards double-slot designs, due to the need for a large heatsink to effectively cool the graphics chipset. As a consequence, the expansion slot below the slot used by the graphics card is effectively blocked and cannot be used. This leaves an ATX quad-graphics system with effectively no expansion slots, as all of the additional slots are blocked by the video cards. The main purpose of Ultra ATX is to overcome this limitation and allow high-end systems to incorporate quad-graphics with additional room for expansion.
WTX Discontinued 2008
Smaller boards
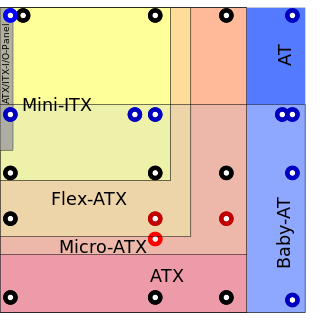
ATX, Mini-ITX, and AT motherboard compatible dimensions and bore positions

ATX motherboard size comparison; rear is on left.
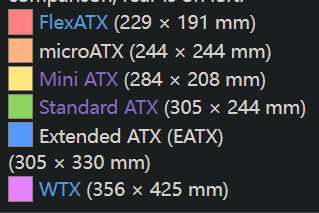
FlexATX (229 × 191 mm)
microATX (244 × 244 mm)
Mini ATX (284 × 208 mm)
Standard ATX (305 × 244 mm)
Extended ATX (EATX) (305 × 330 mm)
WTX (356 × 425 mm)
Other standards for smaller boards (including microATX, FlexATX, nano-ITX, and mini-ITX) usually keep the basic rear layout but reduce the size of the board and the number of expansion slots.
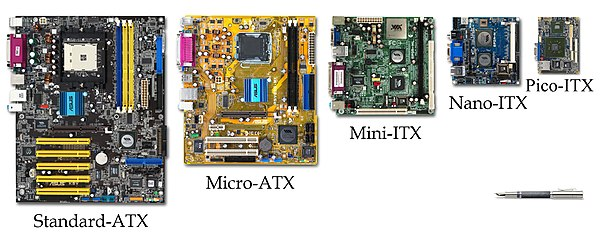
microATX
the popular microATX size removes 2.4 inches (61 mm) and three slots, leaving four.
In computer design, microATX (sometimes referred to as μATX, uATX or mATX) is a standard motherboard form factor introduced in December 1997. The maximum size of a microATX motherboard is 9.6 × 9.6 in (244 × 244 mm).
microATX (µATX、mATX或uMTX)主板标准于1997年12月发表,大小是9.6吋×9.6吋(24.4cmx24.4cm)。它的长度比Standard ATX短20%,Standard ATX标准大小为12×9.6寸。由于长度减少,扩充槽由ATX最多7条减少到4条。
Mini ATX
Mini ATX or Mini-ATX is a generic name that may be used by motherboard manufacturers to describe a small motherboard, and has been used by AOpen in reference to a motherboard design with dimensions 15 × 15 cm (5.9 × 5.9 in).
Mini-ATX motherboards were designed with MoDT (Mobile on Desktop Technology) which adapt mobile CPUs for lower power requirements and less heat generation, which may be beneficial for home theater PCs (HTPC), in-car PCs, or industrial use.
The term miniATX was originally used in (now obsolete versions of) Intel’s ATX specification, and denoted motherboards with dimensions of 284 x 208 mm (11.2 x 8.2 in.), before being abandoned in v2.1 in favor of the microATX specification. The two terms refer to different specifications and should not be conflated.
Mini ITX
As of 2010 Mini ITX has widely replaced FlexATX as the most common small form factor mainboard standard.
INTEL 500 SERIAL CHIPSET
H510
B560
H570
Z590
Z590定位旗舰、H570定位高端、B560定位主流、H510定位入门
字幕前缀现在有:X(最高端的HEDT),Z(消费级的MSDT旗舰),B(主流型号),H(另一个主流型号,不能超频),Q(商用),W(嵌入式,工作站)。 P的话现在已经不用了。
H310:入门级,价格最低,适合家用办公。建议搭配奔腾G5400\G5500这类CPU使用。
B360:主流级,价格适中,适合后缀不带k的CPU。建议搭配酷睿i3-8100\i5-8400\i5-8500\i5-8600\i7-8700等。
H370:中高端,价格稍贵,建议搭配酷睿i7-8700使用。
Z370:高端级,价格贵,能超频,支持4000+高频内存,适合超频玩家。建议搭配i3-8350k/i5-8600k/i7-8700k等后缀带K的CPU。(注:英特尔后缀带k的CPU是可以超频的CPU)
高端主板买华硕;中端主板买技嘉、华擎;AMD主板买微星;入门主板买映泰、七彩虹。
E-ATX型主板是高性能主板,芯片组多为X299、X399,适用于AMD的线程撕裂者、英特尔的i9-7920X等CPU,价格昂贵,很少见。
ATX型主板俗称“大板”,形状类似长方形,这类主板由于更大,所以有更多的插槽和接口,可扩展性较高。比如装双显卡、视频采集卡、PCI网卡等。
M-ATX型主板俗称“小板”,形状接近正方形,这类主板该有的接口都有,不过PCI-E插槽数量较少,可扩展性较小。但价格比大板便宜,预算不多的用户可以选择。
mini-ITX型主板体型更小,这类主板的接口仅属于刚刚够用,几乎没有扩展性,这种主板仅适用于桌面小机箱,较少见。
From system startup to application launching, Intel® Optane™ memory is smart technology that personalizes and accelerates your computing experience on Intel® Core™-based PCs. It learns your most frequently used documents, images, videos, and applications; keeps them handy for quick access; and remembers them—even after powering off the PC.
Intel Turbo Boost is Intel’s trade name for a feature that automatically raises certain versions of its processors’ operating frequency when demanding tasks are running, thus enabling a higher resulting performance.
Generally speaking, the main difference between the two board types is that the Z590 motherboards permit CPU overclocking, whereas the B560 motherboards do not
the Z590 boards tend to have a greater number of PCIe 4.0 slots available.
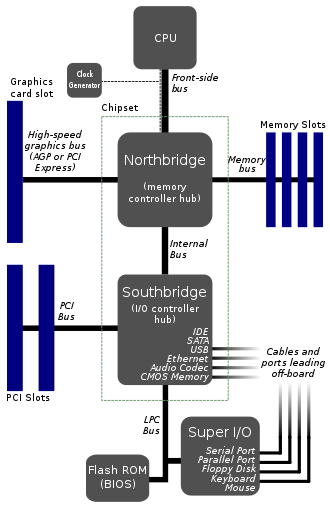
The Platform Controller Hub (PCH) is a family of Intel’s single-chip chipsets, first introduced in 2009. It is the successor to the Intel Hub Architecture, which used two chips - a northbridge and southbridge instead, and first appeared in the Intel 5 Series.
multiple graphics cards and a RAID array of PCIe/NVMe storage, or other bandwidth-hungry hardware into your system, these higher-end platforms are definitely the way to go.
Components
CPU sockets (or CPU slots) in which one or more microprocessors may be installed.
Given the high thermal design power of high-speed computer CPUs and components, modern motherboards nearly always include heat sinks and mounting points for fans to dissipate excess heat.The chipset
The chipset which forms an interface between the CPU, main memory, and peripheral buses
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more ULSI integrated circuits known as a “Data Flow Management System” that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard of computers.
Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors.
Memory slots
into which the system’s main memory is to be installed,BIOS
Read-only memory (ROM), which stores the BIOS that runs when the computer is powered on or otherwise begins execution, a process known as Bootstrapping, or “booting” or “booting up”.
Non-volatile memory chips (usually flash memory in modern motherboards) containing the system’s firmware or BIOS
The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) includes boot firmware and power management firmware. Newer motherboards use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) instead of BIOS.
- Buses
that connect the CPU to various internal components and to expand cards for graphics and sound.
clock generator
The clock generator which produces the system clock signal to synchronize the various components
The CMOS (complementary MOS) battery, which powers the CMOS memory for date and time in the BIOS chip. This battery is generally a watch battery.Power connectors
Power connectors, which receive electrical power from the computer power supply and distribute it to the CPU, chipset, main memory, and expansion cards.
As of 2007, some graphics cards (e.g. GeForce 8 and Radeon R600) require more power than the motherboard can provide, and thus dedicated connectors have been introduced to attach them directly to the power supply.
Power MOSFETs make up the voltage regulator module (VRM), which controls how much voltage other hardware components receive.Slots for expansion cards (the interface to the system via the buses supported by the chipset)
Connectors for hard disk drives, optical disc drives, or solid-state drives, typically SATA and NVMe now
logic and connectors to support commonly used input devices, such as USB for mouse devices and keyboards.
Integrated peripherals
Disk controllers for SATA drives, and historical PATA drives
Historical floppy-disk controller
Integrated graphics controller supporting 2D and 3D graphics, with VGA, DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort, and TV output
integrated sound card supporting 8-channel (7.1) audio and S/PDIF output
Ethernet network controller for connection to a LAN and to receive Internet
USB controller
Wireless network interface controller
Bluetooth controller
Temperature, voltage, and fan-speed sensors that allow software to monitor the health of computer components.
Motherboard connector
PCIe
PCI-Express(peripheral component interconnect express)是一种高速串行计算机扩展总线标准
But outside of PCIe 4.0 SSDs, most devices haven’t taken major advantage of PCIe 4.0 yet.
there’s a limited number of HSIO (high-speed input/output) lanes and PCIe lanes that all of your components must share.
.
many mainstream motherboards compensate for bandwidth limitations by switching some connections off when you install hardware in specific slots.
For example, adding a PCIe M.2 drive may disable some SATA ports, or installing a card in a third PCIe slot may disable a second (or third) M.2 slot, etc.
USB
USB,是英文Universal Serial Bus(通用串行总线)的缩写,是一个外部总线标准,用于规范电脑与外部设备的连接和通讯。是应用在PC领域的接口技术。
Type-A是电脑、电子配件中最广泛的接口标准,鼠标、U盘、数据线上大多都是此接口,体积也最大。
Type-B一般用于打印机、扫描仪、USBHUB等外部USB设备。
Type-C拥有比Type-A及Type-B均小得多的体积,是最新的USB接口外形标准,这种接口没有正反方向区别,可以随意插拔
USB 3.2 Gen 1 – SuperSpeed, 5 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) data signaling rate over 1 lane using 8b/10b encoding (effective 500 MB/s) , the same as USB 3.1 Gen 1 and USB 3.0.
USB 3.2 Gen 2 – SuperSpeed+,[56] 10 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) data rate over 1 lane using 128b/132b encoding (effective 1,212 MB/s), the same as USB 3.1 Gen 2.
USB 3.2 Gen 1×2 – SuperSpeed+, new 10 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) data rate over 2 lanes using 8b/10b encoding (effective 1 GB/s).
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 – SuperSpeed+, new 20 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) data rate over 2 lanes using 128b/132b encoding (effective 2,424 MB/s).
USB-C connectivity, which lets the monitor use a single cable for both video signal and power.
Thunderbolt
Ethernet
Analog audio jack
其他接口
S/PDIF接口是一种数字音频传输接口,全称为Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format,
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
CPU
CPU Socket LGA 1155
LGA全称是Land Grid Array,直译过来就是栅格阵列封装
Supports 1R 2933/ 2666/ 2133 MHz
1DPC 1R Max speed up to 4800+ MHz
1DPC 2R Max speed up to 4266+ MHz
2DPC 1R Max speed up to 4400+ MHz
2DPC 2R Max speed up to 4000+ MHz
Single rank, dual rank and DIMM(s) per channel, respectively.
为了满足笔记本电脑对内存尺寸的要求,SO-DIMM(Small Outline DIMM Module)也开发了出来,它的尺寸比标准的DIMM要小很多,
DIMM全称Dual-Inline-Memory-Modules,中文名叫双列直插式存储模块.
1条单面内存,插DIMM-A2 | 2条单面内存插 DIMM-A2/B2 最高可以跑到4800+
1条双面内存,插DIMM-A2 | 2条双面内存插 DIMM-A2/B2 最高可以跑到4266+
4条单面内存,最高可以跑4400+
4条双面内存,最高可以跑4000+
- 10th Gen Intel Core i7 / i9 processors support 2933 / 2800 / 2666 / 2400 / 2133 natively, others will run at the maximum transfer rate of DDR4 2666MHz.
- 11th Gen Intel processors support 3200 / 2933 / 2800 / 2666 / 2400 / 2133 natively.
CPU后缀代表的意思
英特尔:
1.后缀F表示无核显
2.后缀K代表可以超频。
T:低压版桌面处理器,功耗和性能都比不带后缀的产品低。代表作Core i7-8700T。
X:带有这一后缀的CPU一般都具有王霸之气,基本上就是当代最强桌面级CPU的代号,一般会搭配X99/X299/X399这类平台使用,代表作Core i7-7820X。
AMD:
1.后缀G代表有核显
2.后缀X代表加强版
3.后缀XT代表超级加强版
In computing, Direct Media Interface (DMI) is Intel’s proprietary link between the northbridge and southbridge on a computer motherboard.
In 2021, with the release of 500 series chipsets, Intel increased the amount of DMI 3.0 lanes from four to eight, doubling the bandwidth. [8]
DMI 4.0, set for release in 2021 with 600 series chipsets, will have 8 lanes each providing 16 GT/s, two times faster compared to DMI 3.0 x8.
gigahertz (GHz), or billion cycles per second.
Advantages of Intel Core i5-11500T
Lower power consumption (35W vs 65W), meaning that the rival with higher TDP might require a better cooler or other thermal solution.
Advantages of Intel Core i5-11500
Rocket Lake is Intel’s codename for its 11th generation Core microprocessors. Released on March 30, 2021
Up to 20 CPU lanes of PCI Express 4.0[25]
DDR4-3200 memory support[3]
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2
Optional USB4 / Thunderbolt 4 when paired with Intel JHL8540 Thunderbolt 4 Controller
DMI 3.0 x8 link with Intel 500 Series Chipsets
Graphics card(GPU)
Scalable Link Interface (SLI) is a brand name for a multi-GPU technology developed by NVIDIA for linking two or more video cards together to produce a single output. SLI is an application of parallel processing for computer graphics, meant to increase the processing power available for graphics.
ROG-STRIX-RTX3060-O12G-GAMING
12GB 192-Bit GDDR6
The width of the memory bus through which the graphics data are transferred. The greater the bus width is, the more data the bus can transfer in a clock cycle.
Effective Memory Clock 15 Gbps
The memory type for all current gaming grade video cards is GDDR5, which mostly runs at a real clock frequency of around 1000MHz to around 2000MHz. GDDR5 uses what is called “quad pumped” technology, which within one clock cycle can do four data transfers. Thus the effective memory clock, or data rate, is 1000MHzx4 to 2000MHzx4. This makes comparisons easier.
Core Clock 1882 MHz
The core clock is the speed at which the graphics processor on the card operates, measured in megahertz (MHz).
2 x HDMI 2.1 3 x DisplayPort 1.4a
Multi-Monitor Support 4
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. HDMI supports ?on a single cable ?any uncompressed TV or PC video format, including standard, enhanced, and high-definition video; up to eight channels of compressed or uncompressed digital audio; and a Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) connection.
DisplayPort is a digital display interface standard issued by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) since 2006. It defines a new royalty-free digital audio/video interconnection, intended to be used primarily between a computer and its display monitor, or between a computer and a home-theater system.
3584 CUDA Cores
A CUDA Core is a single process core in NVIDIA GPU chips. The more CUDA Cores a GPU contains, the more powerful it is (also depending on clock speed, memory size, and frequency).
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture),是显卡厂商NVIDIA推出的运算平台。 CUDA™是一种由NVIDIA推出的通用并行计算架构,该架构使GPU能够解决复杂的计算问题。 它包含了CUDA指令集架构(ISA)以及GPU内部的并行计算引擎。
PCI Express 4.0
Interface is the part of the video card that plugs into your computer’s motherboard. It is through interface that your graphics card and computer exchange data. The most common interfaces for video card are PCI Express x16 and x8. PCI Express has undergone several revisions, and the current mainstream revisions are PCI Express 3.0 and PCI Express 4.0. The PCI Express 4.0 is the latest commonly used standard and offers a bandwidth two times that of PCI Express 3.0, while maintaining backward and forward compatibility.
DirectX 12 Ultimate
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms.
OpenGL 4.6
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a cross-language, multi-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU) to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering.
Thermal Design Power
Thermal design power (TDP) is the maximum amount of heat generated by a component in watts that the cooling system needs to dissipate to keep the component in check. It is often a specification for CPU, GPU or system on chip. TDP is not the exact amount of power a component will draw, but can be used as a basic indicator. The higher the TDP, the more power the component will draw from power supply and the more cooling the component will require. To cool the component properly, you need a cooler that is rated at or above the TDP of the component.
Max Resolution 7680 x 4320
HDCP2.2
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP), is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections. Types of connections include DisplayPort (DP), Digital Visual Interface (DVI), and High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), as well as less popular (or now defunct) protocols like Gigabit Video Interface (GVIF) and Unified Display Interface (UDI).The system is meant to stop HDCP-encrypted content from being played on unauthorized devices, or on devices which have been modified to copy HDCP content.
MSI RTX 2060 GAMING Z 6G
6GB 192-Bit GDDR6
Boost Clock 1830 MHz
1 x HDMI 2.0b 3 x DisplayPort 1.4
1920 CUDA Cores
PCI Express 3.0 x16
Radeon RX 5700 XT
PCIe 4.0 x16
video compression standard
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10).
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups of ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics and genomic data, and transmission and file formats for various applications.
DirectX
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms.
Direct3D (the 3D graphics API within DirectX) is widely used in the development of video games for Microsoft Windows and the Xbox line of consoles. Direct3D is also used by other software applications for visualization and graphics tasks such as CAD/CAM engineering. As Direct3D is the most widely publicized component of DirectX, it is common to see the names “DirectX” and “Direct3D” used interchangeably.
DisplayPort HDMI
Data storage
SSD
HDD,Hard Disk Drive的缩写
NAS(Network Attached Storage:网络附属存储)按字面简单说就是连接在网络上,具备资料存储功能的装置,因此也称为“网络存储器”。
SATA(Serial ATA)硬盘,又称串口硬盘,是未来PC机硬盘的趋势,已基本取代了传统的PATA硬盘。SATA的全称是Serial Advanced Technology Attachment,
ESATA是一种数据接口。说到外置存储设备(如移动硬盘)的接口
M.2接口是为超极本(Ultrabook)量身定做的新一代接口标准,以取代原来的mSATA接口。无论是更小巧的规格尺寸,还是更高的传输性能,M.2都远胜于mSATA。
NVM Express(NVMe),或称非易失性内存主机控制器接口规范(英语:Non Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification,缩写:NVMHCIS)
依托于PCIe总线,NVMe设备可适用于各种支持PCIe总线的物理插槽上,包括标准尺寸的PCIe扩展卡(一般是4个PCIe通道)、采用U.2物理连接界面(SFF-8639)的2.5英寸/3.5英寸标准尺寸固态硬盘驱动器、SATA Express总线(兼容于PCIe)的设备、M.2规格扩展卡等。
在NVMe出现之前,高端SSD只得以采用PCI Express总线制造,但需使用非标准规范的接口。若使用标准化的SSD接口,操作系统只需要一个驱动程序就能使用匹配规范的所有SSD。这也意味着每个SSD制造商不必用额外的资源来设计特定接口的驱动程序。
RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks. This is a type of data storage virtualization technology that lumps physical disk drive components together to drive data redundancy and/or improvement.
A RAID card manages a PC’s hard disk drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) so that they work together and drive redundancy and/or performance. It can be hardware (a RAID card) or software.
WD BLUE™ SATA SSD
Form Factor M.2 2280/2.5’’
3D NAND SATA SSD for capacities up to 2TB
3D NAND是英特尔和镁光的合资企业所研发的一种新兴的闪存类型,通过把内存颗粒堆叠在一起来解决2D或者平面NAND闪存带来的限制
Sequential read speeds up to 560 MB/s and sequential write speeds up to 530 MB/s.
interface SATA
WD BLACK SN750 NVME SSD
Thermal Without Heatsink
Interface PCIe
Form Factor m.2 2280
Read speeds up to 3,470 MB/s (1TB models) for improved load times.
sumsung 980 PRO PCIe® 4.0 NVMe® SSD
Interface
PCIe® Gen 4.0 x 4, NVMe® 1.3c
not pcie 4.0
with a PCIe 4.0² interface that’s 2x faster than PCIe 3.0 SSDs³ and 12x faster than Samsung SATA SSDs⁴
- Only Intel 11th Gen processors support PCIe 4.0 x4 mode, this slot will be disabled for other CPUs
Product Type
Form factor of the memory unit
The size, configuration or physical arrangement of drive
NVMe® SSD
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is an open logical-device interface specification for accessing non-volatile storage media attached via PCI Express bus.
M.2 (2280)
Read/Write Speeds
7,000/5,000 MB/s
970 EVO Plus NVMe® M.2 SSD 1TB
HHD
接口的不同也是 SSD 和 eMMC,UFS 的重要区别之一。
一个SSD,为了达到高并行高性能的要求,有多个Flash 芯片,这样就可以在每个芯片上进行相互独立的读写操作,以并行性来提高硬盘吞吐量,还可以增加冗余备份。而手机中为了节省空间和功耗,通常只有一片密度较高的 Flash 芯片。
eMMC 和 UFS 都是面向移动端 Flash 的标准
eMMC 是一个起源较早的技术,全称叫 embedded MultiMedia Card
MMC前面加了个embedded,主要就是为了突出现在这个设备是embedded 在电路板上。eMMC 和 MMC一样,沿用了 8 bit 的并行接口。
用高速串行接口取代了并行接口,而且还是全双工的,也就是可以读写同时进行。所以相比 eMMC, UFS的理论性能提高不少,甚至可以达到一些SSD的水准
Universal Flash Storage (UFS) is a flash storage specification for digital cameras, mobile phones and consumer electronic devices. It was designed to bring higher data transfer speed and increased reliability to flash memory storage, while reducing market confusion and removing the need for different adapters for different types of cards.
M.2插槽也是有两种的,一种是金手指有两个缺口的Socket 2跟金手指只有一个缺口的Socket 3,如上图所示。这两种可以走不同的通道,我们后面会说到。
PCI-E跟SATA3简单说就是数据走的“路”,PCI-E就像是特别宽大的路,数据可以走的特别快,而SATA3与之相比更像是一条崎岖的小路,数据走的特别慢,但是CPU内部就那么大一点,修不了特别多的大路,所以PCI-E通道也就仅有那么几条。
M.2(Socket 2)的固态可以走SATA3或者PCI-E 3.0×2通道(就是两条PCI-E),而M.2(Socket 3)的固态则可以走PCI-E 3.0×4通道;需要说的是每条PCI-E 3.0的带宽是8Gbps,而SATA 3.0的带宽则只有6Gbps。
AHIC是针对SATA这种弯路的交通规则,然后开发者发现,这种针对弯路的规范,数据只能一个一个通过的规则用在宽敞的PCIE通道上面实在太浪费了,于是针对PCIE通道又开发出了NVME规范,可以让很多数据同时通过。
Removable data storage
Optical disc(CD, DVD, Blu-ray)
Flash memory
Floppy disk
Disk pack
Memory
LPDDR内存全称是Low Power Double Data Rate SDRAM,中文意为低功耗双倍数据速率内存,又称为mDDR(Mobile DDR SDRM),是美国JEDEC固态协会面向低功耗内存制定的通信标准,主要针对于移动端电子产品。
手机内存总听过吧,手机参数里4GB/6GB/8GB就是这东西的规格,也就是低功耗内存。
同步动态随机存取内存(synchronous dynamic random-access memory,简称SDRAM)是有一个同步接口的动态随机存取内存(DRAM)。
异步DRAM(asynchronous DRAM)
SDRAM从发展到现在已经经历了五代,分别是:第一代SDR SDRAM,第二代DDR SDRAM,第三代DDR2 SDRAM,第四代DDR3 SDRAM,第五代,DDR4 SDRAM。
G 是英文‘专门’的第一个字母 在显卡上意思就是为显卡专门DDR内存
DDR=Double Data Rate双倍速率,DDR SDRAM=双倍速率同步动态随机存储器,人们习惯称为DDR,其中,SDRAM 是Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory的缩写,即同步动态随机存取存储器。
加装了马甲的内存条与普通内存条相比是加装了散热模块,比普通内存条有更好的散热性能。
ddr4
Standard transfer rates are 1600, 1866, 2133, 2400, 2666, 2933, and 3200 MT/s
Channel Supported Dual Channel
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual, triple, and quad-channel memory employ two, three, and four channels respectively.
NAND Flash
The type of flash memory in the device
Samsung V-NAND 3-bit MLC
Sequential Read Speed
Up to 3,500 MB/s
Sequential Write Speed
Up to 3,300 MB/s
Cache Memory
Samsung 1GB Low Power DDR4 SDRAM
CMK16GX4M2Z3200C16
\
288-Pin DDR4 SDRAM
Currently there are four major types of server memory available on the market: the latest DDR4 SDRAM, DDR3, DDR2 ,and the relatively dated DDR1. A server system can only take the kind of memory is was designed to take. Mixing different types of memory in a system is unworkable, and may cause hardware damage.
Speed
DDR4 3200 (PC4 25600)
Standards
DDR4-1600 (PC4-12800)
DDR4-1866 (PC4-14900)
DDR4-2133 (PC4-17000)
DDR4-2400 (PC4-19200)
DDR4-2666 (PC4-21333)
DDR4-2933 (PC4-23466)
DDR4-3200 (PC4-25600)
CAS Latency 16
Column Address Strobe (CAS) latency, or CL, is the delay time between the moment a memory controller tells the memory module to access a particular memory column on a RAM module, and the moment the data from the given array location is available on the module’s output pins. In general, the lower the CL, the better.
NAND
It is typically a type of dynamic RAM (DRAM), such as synchronous DRAM (SDRAM),
Attribute NAND NOR
Main application File storage Code execution
Storage capacity High Low
Cost per bit Low
Active power Low
Standby power Low
Write speed Fast
Read speed Fast
Execute in place (XIP) No Yes
Reliability High
Power Supply (PSU)
A power supply unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer.
Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power supplies.
Dimensions of an ATX power supply are 150 mm width, 86 mm height, and typically 140 mm depth, although the depth can vary from brand to brand.
Power rating
The overall power draw on a PSU is limited by the fact that all of the supply rails come through one transformer and any of its primary side circuitry, like switching components.
Total power requirements for a personal computer may range from 250 W to more than 1000 W for a high-performance computer with multiple graphics cards. Personal computers without especially high performing CPUs or graphics cards usually require 300 to 500 W.
Power supplies are designed around 40% greater than the calculated system power consumption. This protects against system performance degradation, and against power supply overloading.
Power supplies label their total power output, and label how this is determined by the electric current limits for each of the voltages supplied.
The system power consumption is a sum of the power ratings for all of the components of the computer system that draw on the power supply.
Efficiency
Power Supply Connectors
Typically, power supplies have the following connectors (all are Molex (USA) Inc Mini-Fit Jr, unless otherwise indicated):
ATX motherboard power connector (usually called P1): This is the connector that goes to the motherboard to provide it with power. The connector has 20 or 24 pins. One of the pins belongs to the PS-ON wire (it is usually green). This connector is the largest of all the connectors. In older AT power supplies, this connector was split in two: P8 and P9. A power supply with a 24-pin connector can be used on a motherboard with a 20-pin connector. In cases where the motherboard has a 24-pin connector, some power supplies come with two connectors (one with 20-pin and other with 4-pin, i.e. 20+4-pin form) which can be used together to form the 24-pin connector.
12V only power connector (labelled P1, though it is not compatible with the ATX 20 or 24 pin connector): This is a 10 or 16-pin Molex connector supplying the motherboard with three or six 12 V lines with common returns, a ‘supply OK’ signal, a ‘PSU ON’ signal and a 12 or 11 V auxiliary supply. One pin is left unused.[34]
12V only System monitoring (P10): This is a 171822-8 AMP or equivalent connector carrying a supply to the PSU fan and sense returns.[34]
ATX12V 4-pin power connector (also called the P4 power connector). A second connector that goes to the motherboard (in addition to the 24-pin ATX motherboard connector) to supply dedicated power for the processor.
4+4-pin For the purpose of backwards compatibility, some connectors designed for high-end motherboards and processors, more power is required, therefore EPS12V has an 8-pin connector.
4-pin peripheral power connector
4-pin Peripheral power connectors: These are the other, smaller connectors that go to the various disk drives of the computer. Most of them have four wires: two black, one red, and one yellow. Unlike the US standard mains electrical wire color-coding, each black wire is a ground, the red wire is +5 V, and the yellow wire is +12 V. In some cases these are also used to provide additional power to PCI cards such as FireWire 800 cards.
4-pin Molex (Japan) Ltd power connectors (usually called Mini-connector, mini-Molex, or Berg connector): This is one of the smallest connectors that supplies a 3.5-inch floppy drive with power. In some cases, it can be used as an auxiliary connector for Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) video cards. Its cable configuration is similar to the Peripheral connector.
Auxiliary power connectors: There are several types of auxiliary connectors, usually in 6-pin form, designed to provide additional power if it is needed.
Serial ATA power connectors: a 15-pin connector for components that use SATA power plugs. This connector supplies power at three different voltages: +3.3, +5, and +12 V, in three pins per wire, one designed to precharge capacitive loads on for hot-plugging designed backplanes.
6-pin Most modern computer power supplies include six-pin connectors that are generally used for PCI Express graphics cards, but a newly introduced eight-pin connector should be seen on the latest model power supplies. Each PCI Express 6-pin connector can output a maximum of 75 W.
6+2-pin For the purpose of backwards compatibility, some connectors designed for use with high end PCI Express graphics cards feature this kind of pin configuration. It allows either a six-pin card or an eight-pin card to be connected by using two separate connection modules wired into the same sheath: one with six pins and another with two pins. Each PCI Express 8-pin connector can output a maximum of 150 W.
12-pin for PCI Express graphics cards, each PCI Express 12-pin connector can output a maximum of 648 W (12V, 9A), 2 150 W 8-pin can be combined via an adapter cable to form one 648 W 12-pin.
16-pin (12VHPWR) for PCI Express graphics cards, each PCI Express 16-pin connector can output a maximum of 662 W (12V, 9.2A), 12 power pins, 4 contact pins. Introduced on ATX 3.0.
An IEC 60320 C14 connector with an appropriate C13 cord is used to attach the power supply to the local power grid.
ATX specification for power supply
ATX power supplies generally have the dimensions of 150 × 86 × 140 mm (5.9 × 3.4 × 5.5 in)
That last dimension, the 140 mm depth, is frequently varied, with depths of 160, 180, 200 and 230 mm used to accommodate higher power, larger fan and/or modular connectors.
The ATX specification requires the power supply to produce three main outputs, +3.3 V, +5 V and +12 V. Low-power −12 V and +5 VSB (standby) supplies are also required.
The −12 V supply is primarily used to provide the negative supply voltage for RS-232 ports and is also used by one pin on conventional PCI slots primarily to provide a reference voltage for some models of sound cards.
The 5 VSB supply is used to produce trickle power to provide the soft-power feature of ATX when a PC is turned off, as well as powering the real-time clock to conserve the charge of the CMOS battery.
ATX power supply revisions
Original ATX
ATX, introduced in late 1995, defined three types of power connectors:
4-pin “Molex connector” – transferred directly from AT standard: +5 V and +12 V for P-ATA hard disks, CD-ROMs, 5.25 inch floppy drives and other peripherals.
4-pin Berg floppy connector – transferred directly from AT standard: +5 V and +12 V for 3.5 inch floppy drives and other peripherals.
20-pin Molex Mini-fit Jr. ATX motherboard connector – new to the ATX standard.
A supplemental 6-pin AUX connector providing additional 3.3 V and 5 V supplies to the motherboard, if needed. This was used to power the CPU in motherboards with CPU voltage regulator modules which required 3.3 volt and/or 5 volt rails and could not get enough power through the regular 20-pin header.
The power distribution specification defined that most of the PSU’s power should be provided on 5 V and 3.3 V rails, because most of the electronic components (CPU, RAM, chipset, PCI, AGP and ISA cards) used 5 V or 3.3 V for power supply. The 12 V rail was only used by computer fans and motors of peripheral devices (HDD, FDD, CD-ROM, etc.)
ATX 3.0
The specifications for ATX 3.0 were released in February 2022.
af
逆变器是把直流电能(电池、蓄电瓶)转变成定频定压或调频调压交流电(一般为220V,50Hz正弦波)的转换器。
alternating current (AC) electric power to low-voltage direct current (DC) power
A power supply unit (PSU) converts alternating current (AC) electric power to low-voltage direct current (DC) power for the computer. Laptops can run on built-in rechargeable battery. The PSU typically uses a switched-mode power supply (SMPS), with power MOSFETs (power metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) used in the converters and regulator circuits of the SMPS.
VRM stands for voltage regulator module. Some modern CPUs and GPUs (aka graphics cards) use VRMs to control and lower the voltage (V) sent to these components in order to avoid exceeding their maximum voltage capabilities. VRMs are especially important for overclocking a CPU or GPU. In theory, VRMs should mean the power supplied to the component is consistent and steady.
SuperNOVA 750 GA
Type ATX12V
Maximum Power 750W
Modular Full Modular
A modular power supply provides a detachable cable system, offering the ability to remove unused connections at the expense of a small amount of extra electrical resistance introduced by the additional connector. This reduces clutter, removes the risk of dangling cables interfering with other components, and can improve case airflow. Many modular supplies have some permanent multi-wire cables with connectors at the ends, such as PC main and 4-pin Molex, though newer supplies marketed as “Fully Modular” allow even these to be disconnected..
Energy-Efficient 80 PLUS GOLD Certified
MTBF >100,000 Hours
Life span is usually specified in mean time between failures (MTBF), where higher MTBF ratings indicate longer device life and better reliability. Using higher quality electrical components at less than their maximum ratings or providing better cooling can contribute to a higher MTBF rating because lower stress and lower operating temperatures decrease component failure rates.
Main Connector 24Pin
The main power connector is used to directly connect the motherboard and the PSU. Two types of main power connectors are often utilized in today’s PSU: the 20-pin and 24-pin formats. To provide compatibility with older motherboards featuring 20-pin power socket designs, some PSUs provide 20+4-pin main power connector. This type of power connector is very versatile, and can easily be used with both 20-pin and 24-pin motherboard. There are more and more motherboards providing 24-pin power connector socket (many motherboards with 24-pin socket can still work with 20-pin power supplies).
+12V Rails Single
The +12v is the main power your computer uses. CPU, motherboard and VGA card, along with others components, use it to run. The higher current the 12v rails can offer, the more wattage it can output. Special attention should be paid to the +12v spec if you want to build a SLI/CrossFire setup with multiple VGA cards.
PCI-Express Connector 6 x 6+2-Pin
ncludes 6-pin, 8-pin, and 6+2-pin, for use with high-end video cards. Each PCI Express 6-pin connector can output a maximum of 75 W. And each PCI Express 8-pin (6+2-pin) connector can output a maximum of 150 W.
SATA Power Connector 8
A 15-pin connector for components which use SATA power plugs. This connector supplies power at three different voltages: +3.3, +5, and +12 volts.
1 x 24 Pin ATX
2 x 8pin(4+4) EPS (CPU)
The EPS connector is meant to supply power to a motherboard cpu socket
6 x 8pin(6+2) PCIe
9 x SATA
4 x Four-Pin Peripheral
1 x Floppy
floppy disk的接口。
也叫软驱
Case机箱 风扇
A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, is the enclosure that contains most of the hardware of a personal computer.
The components housed inside the case (such as the CPU, motherboard, memory, mass storage devices, power supply unit and various expansion cards) are referred as the internal hardware,
while hardware outside the case (typically cable-linked or plug-and-play devices such as the display, speakers, keyboard, mouse and USB flash drives) are known as peripherals.
peripheral/pəˈrɪfərəl/
附带的
not as important as the main aim, part, etc. of sth
Case sizes and shapes
Cases can come in many different sizes and shapes, which are usually determined by the form factor of the motherboard since it is physically the largest hardware component in most computers.
Consequently, personal computer form factors typically specify only the internal dimensions and layout of the case.
Tower cases are often categorized as mini-tower, midi-tower, mid-tower, or full-tower. The terms are subjective and inconsistently defined by different manufacturers.
Full tower cases are typically 56 cm (22 in) or more in height and intended to stand on the floor. They can have anywhere from six to ten externally accessible drive bays.
However, as computing technology moves from floppy disks and CD-ROMs to large capacity hard drives, USB flash drives, and network-based solutions, more recent full tower cases typically only have none, one, or two external bays for CD drives, with the internal bays moved elsewhere in the case to improve airflow.
Today, full tower cases are commonly used by enthusiasts as showpiece display cases with custom water cooling, lighting, and tempered glass (replacing acrylic).
Mid-tower cases are smaller, about 46 cm (18 in) high with two to four external bays.
A mini-tower case will typically have only one or two external bays.
The marketing term midi-tower sometimes refers to cases smaller than mid-tower but larger than mini-tower, typically with two to three external bays.
qgasvgsgdf
塔式机箱(Tower case),即通常说的立式机箱。塔式机箱按照大小可分为全塔、中塔和mini塔三类,不过业界并没有在大小方面就此形成统一的分类标准。通常全塔机箱拥有4个以上的光驱位,中塔机箱拥有3-4个光驱位,而mini塔仅有1-2个光驱位。
Obsidian Series 750D
Type ATX Full Tower
External 5.25 Drive Bays 3
Internal 3.5 Drive Bays 6 x Combo 3.5” / 2.5”
Internal 2.5 Drive Bays 4
Fan Options Front: 2 x 120mm / 2 x 140mm fan (2 x 140mm fan included)
Rear: 1 x 140mm fan (included)
Top: 3 x 120mm / 2 x 140mm fan
Bottom: 2 x 120mm fan
Radiator Options
Front: 240/280mm
Top: 240/280/360mm
Rear: 120/140mm
Bottom: 120/240mm
For case fans go for 140mm fans that has the letters AF in them since that stands for AirFlow
For the radiator you will 95% of the time want to have fans that has the letters SP in them since that stands for Static Pressure.
There are two main stats for a fan. There’s the CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating, which describes how good it is at moving air when there isn’t any obstruction. There’s also static pressure, which describes how good it is at forcing air through obstructions. On a radiator, you need high static pressure, and for case fans, you want high CFM
in order to make your CPU achieve higher clock speeds than it’s rated for out of the box, you’ll likely spend extra on an enhanced cooling system and a high-end motherboard. By the time you factor in all these extra costs, you may be better off budgeting another $50-$100 (£40-80) for a CPU that comes with higher clock speeds out of the box.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi uses multiple parts of the IEEE 802 protocol family and is designed to interwork seamlessly with its wired sibling Ethernet.
IEEE 802.11b: 5.5 Mbit/s and 11 Mbit/s, 2.4 GHz standard (1999)
IEEE 802.11a: 54 Mbit/s, 5 GHz standard (1999, shipping products in 2001)
IEEE 802.11g: 54 Mbit/s, 2.4 GHz standard (backwards compatible with b) (2003)
IEEE 802.11n: Higher Throughput WLAN at 2.4 and 5 GHz; 20 and 40 MHz channels; introduces MIMO to Wi-Fi (September 2009)IEEE 802.11n-2009 or 802.11n is a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The Wi-Fi Alliance has also retroactively labelled the technology for the standard as Wi-Fi 4. It standardized support for multiple-input multiple-output, frame aggregation, and security improvements, among other features, and can be used in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.
a single-band router operates on the (somewhat) newer 802.11n standard, also known as “Wireless-N.” Wireless-N routers on a 2.4 GHz band offer theoretical speeds of up to 800 Mbps—“theoretical” meaning that you’ll probably never see these speeds during day-to-day use, given real-world factors such as your Internet service limitations.
IEEE 802.11ac-2013 or 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard in the 802.11 set of protocols (which is part of the Wi-Fi networking family), providing high-throughput wireless local area networks (WLANs) on the 5 GHz band.[a] The standard has been retroactively labelled as Wi-Fi 5 by Wi-Fi Alliance.
In addition to supporting the 2.4 GHz Wireless-N standard, dual-band routers support the 5 GHz frequency band, operating on the newer 802.11ac standard. At their theoretical best, that means they support aggregate speeds up to 2,167 Mbps or more.
Beamforming is a radio wave technology that is written into the next generation IEEE Wi-Fi 802.11ac standard. This technology allows the beamformer (Router) to transmit radio signal in the direction of the beamformee (Client), thus creating a stronger, faster and more reliable wireless communication.
Think of beamforming as a radio transmission from the transmitter to the receiver, customized according to their relative locations. A NETGEAR router with Beamforming+ scans the entire wireless network, understands the parametric of each client, and optimizes the Wi-Fi communication with each client by transmitting focused and directional radio signals.
802.11ac-class device wireless speeds are often advertised as AC followed by a number, that number being the highest link rates in Mbit/s of all the simultaneously-usable radios in the device added up. For example, an AC1900 access point might have 600 Mbit/s capability on its 2.4 GHz radio and 1300 Mbit/s capability on its 5 GHz radio. No single client device could connect and achieve 1900 Mbit/s of throughput, but separate devices each connecting to the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios could achieve combined throughput approaching 1900 Mbit/s.
802.11ac Wave1,确实没什么好介绍的,它就是还没有引入MU-MIMO技术、4空间流以及160MHz频宽的初代802.11ac标准。不过相较于802.11n,在无线传输速率方面,初代11ac依然可以倚靠着新的256QAM调制方式和新的80MHz频宽做到秒杀。
IEEE 802.11ax: High Efficiency WLAN at 2.4, 5 and 6 GHz; introduces OFDMA to Wi-Fi(February 2021)IEEE 802.11ax-2021 or 802.11ax is an IEEE standard for wireless local-area networks (WLANs) and the successor of 802.11ac. It is marketed as Wi-Fi 6 [2.4 GHz and 5 GHz] and Wi-Fi 6E [6 GHz] by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It is also known as High Efficiency Wi-Fi, for the overall improvements to Wi-Fi 6 clients under dense environments. It is designed to operate in license-exempt bands between 1 and 7.125 GHz, including the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands already in common use as well as the much wider 6 GHz band (5.925–7.125 GHz in the US).The main goal of this standard is enhancing throughput-per-area in high-density scenarios, such as corporate offices, shopping malls and dense residential apartments. While the nominal data rate improvement against 802.11ac is only 37%,:qt the overall throughput improvement (over an entire network) is 400% (hence High Efficiency).:qt This also translates to 75% lower latency.
Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for multipath wireless communication, in which multiple users or terminals, each radioing over one or more antennas, communicate with one another.
Mesh WiFi or Whole Home WiFi systems consists of a main router that connects directly to your modem, and a series of satellite modules, or nodes, placed around your house for full WiFi coverage. They are all part of a single wireless network and share the same SSID and password, unlike traditional WiFi routers.
Comparing range extenders to whole home WiFi is like comparing apples to oranges. Range extenders are certainly effective when it comes to increasing the range of your router, but they do so at the expense of WiFi performance, which gets cut in half.
You might also experience connection issues when jumping from the router to the extender, because you’ll need to switch networks manually.
BLUETOOTH
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) are the three security and security certification programs developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks. The Alliance defined these in response to serious weaknesses researchers had found in the previous system, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).[1]
An RF module (short for radio-frequency module) is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices.
Several carrier frequencies are commonly used in commercially available RF modules, including those in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands such as 433.92 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2400 MHz.
在无线电发射设备,包括手机(具有Wi-Fi或者蓝牙功能),蓝牙耳机,无线路由器,无线网卡等无线产品上均有体现。
CMIIT ID即无线电发射设备型号核准代码。
只有带有我国无线电发射设备型号核准代码的无线电发射设备才是可以在我国国内销售和使用的无线电发射设备。
The network connection style used in classic Bluetooth is a traditional point-to-point connection that looks like the hub-and-spoke model known as a star topology. Devices can only talk to the central controller and not directly to each other. Therefore, the hub must relay message traffic between devices if that is needed for the application.
In 2010, a new version of Bluetooth (Bluetooth 4.0) was introduced, known as Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) or Bluetooth Smart.
BLE added a point-to-multipoint/ broadcast model that is useful for a short-range navigation beacon mode
路由器
互联网业务
internet service
互联网行业的创新业务:人工智能,物联网,云
ISP( 接入服务提供商)
内容服务提供商 ICP
RJ是Registered Jack的缩写,意思是“注册的插座”。在FCC(美国联邦通信委员会标准和规章)中RJ是描述公用电信网络的接口,计算机网络的RJ45是标准8位模块化接口的俗称
在家用的ADSL Modem(调制解调器)上还会有RJ11接口,它比RJ45接口略小,主要用来连接电话线使用。需要说明的是,RJ11接口为4或6针,而RJ45则为8针接口,所以RJ45插头不能插入RJ11接口,反之RJ11插头也不能插入RJ45接口(虽然在物理接口上是可以实现的)
为达到最佳兼容性,制作直通线时一般采用T568B标准.网络传输线分为直通线、交叉线和全反线。直通线用于异种网络设备之间的互连,例如,计算机与交换机。交叉线用于同种网络设备之间的互连,例如,计算机与计算机。
平衡了千兆与万兆的2.5千兆网卡,2.5G网卡具有高达2500Mbps的传输速率,是千兆网卡速度的2.5倍
无线通信
Wireless USB was a short-range, high-bandwidth wireless radio communication protocol
USB(universal serial bus,通用串行总线)作为一个计算机与外设之问的接口方案,因其具有使用方便、传输速度快、端口易扩展等特点,
The standard is now obsolete, and no new hardware has been produced for many years
超宽带(UWB,Ultra Wide Band)
WPAN的目标是用无线电或红外线代替传统的有线电缆,以低价格和低功耗在10m范围内实现个人信息终端的智能化互联,组建个人化信息网络。其最普遍的应用是连接电脑、打印机、无绳电话、PDA以及信息家电等设备。实现WPAN的主要技术有:IEEE802.11b(Win)、Home RF、IrDA、蓝牙(Bluetooth)以及超宽带等五种。
蓝牙Mesh网络是用于建立多对多(many:many)设备通信的低能耗蓝牙(Bluetooth Low Energy,也称为Bluetooth LE)新的网络拓扑。
ZigBee译为”紫蜂”,是一种低速短距离传输的无线网上协议,。主要特色有低速、低耗电、低成本、短时延,高容量
ZigBee的响应速度较快,一般从睡眠转入工作状态只需15ms,节点连接进入网络只需30ms,进一步节省了电能。相比较,蓝牙需要3~10s、
而蓝牙则是两台设备之间相互进行数据传输,是一种点对点的连接方式。从这方面看起来,蓝牙的数据安全性更高一些。 其次,由于蓝牙使用的是微带天线,体积小,方便集成到设备中,而且蓝牙模块成本很低,因此蓝牙设备的普及率非常高
免执照频段。使用工业科学医疗(ISM)频段
RoHS是由欧盟立法制定的一项强制性标准,它的全称是《关于限制在电子电气设备中使用某些有害成分的指令》(Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
该标准的目的在于消除电器电子产品中的铅、汞、镉、六价铬、多溴联苯和多溴二苯醚(注意:PBDE正确的中文名称是指多溴二苯醚,多溴联苯醚是错误的说法)共6项物质,并重点规定了镉的含量不能超过0.01%。
OFDM(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)即正交频分复用技术,实际上OFDM是MCM(Multi Carrier Modulation),多载波调制的一种。
多载波调制(Multicarrier Modulation)采用了多个载波信号。它把数据流分解为若干个子数据流,从而使子数据流具有低得多的传输比特速率,利用这些数据分别去调制若干个载波。
基带:Baseband 信源(信息源,也称发射端)发出的没有经过调制(进行频谱搬移和变换)的原始电信号所固有的频带(频率带宽),称为基本频带,简称基带。
无线Mesh组网的原理,是主路由通过WiFi和子路由进行通信,从而完成数据的传输。如何WiFi信号弱或者无法覆盖,那么子路由也无法带来畅快的上网体验。
使用电力线组网,用户最怕的组网性能衰减问题。在实际使用中网络传输当家中使用微波炉、电暖气等大功率电器时,通过电力线的网络传输就会变慢。
Power-line communication (also known as power-line carrier or PLC) carries data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers.
。
G.hn is a specification for home networking with data rates up to 2 Gbit/s and operation over four types of legacy wires: telephone wiring, coaxial cables, power lines and plastic optical fiber.
HomePlug is the family name for various power line communications specifications under the HomePlug designation,
Electromagnetic interference
One of the concerns with all powerline systems, when compared to dedicated data wiring, is that the route of the wiring is not known in advance, and is generally already optimized for power transmission. This means that there will be situations where the system will radiate a significant fraction of the energy, in the form of radio frequency interference, or be vulnerable to the ingress of external signals.
PA(功率放大器)有效增强信号发射功率,
LNA(低噪声放大器)可以提高信号接收灵敏度。在放大微弱信号的场合,放大器自身的噪声对信号的干扰可能很严重,因此希望减小这种噪声,以提高输出的信噪比。低噪声放大器, 噪声系数很低的放大器。一般用作各类无线电接收机的高频或中频前置放大器,
LDPC是Low Density Parity Check Code英文缩写,意思是低密度奇偶校验码
近场通信(Near Field Communication,简称NFC),是一种新兴的技术,使用了NFC技术的设备(例如移动电话)可以在彼此靠近的情况下进行数据交换,是由非接触式射频识别(RFID)及互连互通技术整合演变而来的,通过在单一芯片上集成感应式读卡器、感应式卡片和点对点通信的功能,利用移动终端实现移动支付、电子票务、门禁、移动身份识别、防伪等应用。
NFC标准为了和非接触式智能卡兼容,规定了一种灵活的网关系统,具体分为三种工作模式:点对点通信模式、读写器模式和NFC卡模拟模式。
近距无线通信技术除NFC外,主要还包括射频识别(RFID)、蓝牙(Bluetooth)、紫蜂(ZigBee)、红外、 Wi-Fi等技术。
NFC 技术具有极高的安全性,在短距离通信中具有性能优势,更重要的是成本较低,因此自其 2003 年问世以来,得到众多企业的关注和支持。
射频识别(RFID)是 Radio Frequency Identification 的缩写。
RFID技术的基本工作原理并不复杂:标签进入阅读器后,接收阅读器发出的射频信号,凭借感应电流所获得的能量发送出存储在芯片中的产品信息(Passive Tag,无源标签或被动标签),或者由标签主动发送某一频率的信号(Active Tag,有源标签或主动标签),阅读器读取信息并解码后,送至中央信息系统进行有关数据处理。
小米空白门卡是小米手机基于NFC的功能之一,让用户可以摆脱实体门卡的束缚。不过也有用户会遇到门卡无法模拟的情形。这种情形不是因为门卡频率不符,就是因为被加密了。这时候就需要使用小米空白门卡功能了。
虚位密码在用法上就用最简单的方法补足了这三个缺点,正确密码长度和内容不变,在正确密码前后加入随意按下的数字,只要整串数字中有完整且未拆分的正确的密码,就可以通过验证。
projection
120寸16:9幕布尺寸为2.6*1.5米,
幕布的大小=投影距离/( 0.87 X 0.0254 X 投射比)。
有了上面这个公式可以做以下计算:
可以很快的算出多远的距离配多大的幕布了,比如,要投2米远,投影仪的投射比是1.2,幕布最小要买多大尺寸的?
幕布的大小=2 / (0.87X0.0254X1.2)=75寸。
当然也可以根据幕布画面尺寸算投影距离。买的幕布画面尺寸是80寸,投影仪的投射比是1.2,那么投影距离是多少?
投影距离=80X 0.87 X 0.0254 X 1.2=2.12米。
当然,也可以很快算出什么空间配什么投射比的投影仪?比如,想在2.5米远的距离实现100寸的画面,选什么样的投影仪。
投射比=2.5 / (100X0.87X0.0254)=1.13
投射比=投影距离/画面宽度。从这个公式可以看出:该比值越小,说明相同投影距离,投射画面的宽度越大。普通投影机的投射比,通常在1.5-1.9之间。当投射比小于1时,为短焦镜头; 而当投射比达到0.6以下,为超短焦镜头。
如果投射比是一个定值,则表示投影距离固定时,画面大小也固定了,只能调整镜头进行聚焦,但是画面大小不能变化。
There are three main technologies used for projection – DLP, LCD and LED. DLP (Digital Light Processing) uses a chip made of tiny microscopic mirrors and a spinning colour wheel to create an image. DLP projectors deliver sharp images, don’t need any filters, have a better response time as well as 3D capabilities. The effective lamp life of a DLP projector is only 2000-5000 hours and some people see colour ghosting/banding in some scenes. On the other hand, LCD projectors use liquid crystal displays, have no moving parts and thus are generally less expensive. If you are on a budget a single chip LCD projector is ideal while 3-chip LCDs offer better colour saturation, lower noise levels and work better for movies. However, LCDs require constant filter maintenance and output less contrast. The LEDs in LED projectors have a lifespan of over 20,000 hours. They deliver better colours, have lower power consumption and virtually zero maintenance costs. Also, LED projectors are smaller and generate less heat. Do keep in mind that LED projectors have limited brightness compared to LCD or DLP so they are not recommended if your room has a lot of ambient light.
5,000 hours is still over three years of use at four hours a night.
Trigger OUT接口(12V DC输出)对于家庭影院应用来说具有很高的实用价值,主要用于触发电动屏幕或照明控制等外部设备。在打开投影机的时候,幕布会自动放下,照明设备会自动关闭;当关闭投影机时,幕布则会自动收起,照明设备会自动开启,充分享受到智能家居带来的乐趣。
USB接口确实可以传输音频与视频信号,通用性好于VGA接口。但是,此功能在应用中具有一定局限性,传输音视频时可能会出现一些延迟,因此更适合以PPT、图片为主的商务演示。目前,爱普生、富可视均有部分投影机提供USB传输功能,让你在商务演示之前,不用再苦苦寻觅VGA线,拿一根常见的USB线就足够了。
网络接口
网络投影功能,投影机在接入网络后,可以直接访问指定电脑的IP地址,将电脑画面通过网络直接投影出来。
Monitor(Screen)显示器
A light-emitting diode (LED)
Liquid-crystal display (LCD)
Organic light-emitting diode (OLED)
A quantum dot display is a display device that uses quantum dots (QD),
AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, /ˈæmoʊˌlɛd/) is a type of OLED display device technology.
Cathode-ray tube (CRT)
High-dynamic-range (HDR)
standard-dynamic-range (SDR)
Hybrid log–gamma (HLG) is a backwards-compatible high dynamic range (HDR) standard
HLG是最广泛,推广成本最低,接受度也最高的。
HDR 10次之。
Dolby Vision最高端,不是一用户能接触到的,
显示技术
AMD FreeSync and Nvidia G-Sync both allow the monitor and the graphics card to coordinate the refresh rate of the screen with the output of the GPU,
a given monitor will likely provide support for only one or the other format.
LDPC是Low Density Parity Check Code英文缩写,意思是低密度奇偶校验码
FHD意思是全高清,即FULL HD,全称为Full High Definition。一般能达到分辨率1920*1080
HD(分辨率<=1280*720)
UHD根据国际电信联盟(ITU)发布的“超高清UHD”标准的建议是,屏幕的物理分辨率达到38402160(4K2K)及以上的显示称之为超高清,是普通FullHD(1920*1080)宽高的各两倍,面积的四倍。
LCD投影机按内部液晶板的片数可分为单片式和三片式两种,现代液晶投影机大都采用3片式LCD板。三片式LCD投影机是用红、绿、蓝三块液晶板分别作为红、绿、蓝三色光的控制层。
DLP是“Digital Light Processing”的缩写,即为数字光处理,也就是说这种技术要先把影像信号经过数字处理,然后再把光投影出来。它是基于TI(美国德州仪器)公司开发的数字微镜元件——DMD(Digital Micromirror Device)来完成可视数字信息显示的技术。说得具体点,就是DLP投影技术应用了数字微镜晶片(DMD)来作为主要关键处理元件以实现数字光学处理过程。
LCOS(Liquid Crystal on Silicon),即液晶附硅,也叫硅基液晶,是一种基于反射模式,尺寸非常小的矩阵液晶显示装置。这种矩阵采用CMOS技术在硅芯片上加工制作而成。
1、3LCD优势在于亮度和易于安装,而DLP优势在于灰阶以及3d无串扰。DLP比3LCD总体而言更进步一些。
2、对于遮光良好有合适幕布的用DLP会达到出色的效果,例如家用的,卧室用的投影仪。
3、对于遮光不良而且投的画面又比较大的有时只能选择3LCD,例如办公室用的,教室用的传统投影仪。
色域
Wide color gamut (WCG)
色域(Color Space),又被称为色彩空间,它代表了一个色彩影像所能表现的色彩具体情况,Adobe RGB是由Adobe公司推出的色域标准,sRGB是由惠普与微软公司于1997年共同开发的,其中“S”可解释为“标准”(Standard)。Adobe RGB较之sRGB有更宽广的色彩空间,它包含了sRGB所没有的CMYK色域,层次较丰富,但色彩饱和较低。sRGB对于绿色部分色域覆盖非常少。这个就导致一个很严重的问题,那就是对花草森林等场景的色彩表现力不足。也正是因为这样,它对显示器的要求不高,所以现在市面上大多数显示器都能达到sRGB100%。
P3 色域广义上包含了 DCI-P3 和 Display P3, 前者是影视行业标准,Display P3 是 Apple 在 DCI-P3 基础上参考了 sRGB 而修订出的自己的标准,在白点和伽马上与 DCI-P3 不同,但是能覆盖的颜色相同,相对于 sRGB 除了蓝色都有较大提升。
DCI-P3是一种应用于数字影院的色域,它是一种以人类视觉体验为主导的色域标准,最新的标准为Rec.2020
DCI-P3是一款更加注重于视觉冲击,而不是色彩全面性的色域。并且相对其他色彩标准,它拥有更广阔的红色/绿色系色彩范围。
Digital Cinema Initiatives, LLC (DCI) is a consortium of major motion picture studios, formed to establish specifications for a common systems architecture for digital cinema systems.
Rec.709是1990年国际电信联盟指定的HDTV的统一色彩标准,它的色彩范围和用于互联网媒体的sRGB色彩空间几乎相同。DCI-P3是美国电影行业推出的一种广色域标准,也是目前数字电影回放设备的色彩标准之一,它呈现的色域相比Rec.709色域大了25%,主要是绿色和红色的范围更广。BT.2020则是国际电信联盟针对超高清UHD(4K及8K)视频制作与显示系统指定的一个标准,这个标准涵盖了分辨率、色域、色深等很多指标,其中色域方面其相比Rec.709具有更大的范围,甚至超过了DCI-P3。
ITU international telecommucication uion
REC RECOMMENDATION
NTSC是National Television Standards Committee (美国)国家电视标准委员会.NTSC色域指的是NTSC标准下的颜色的总和
目的是为了给当时刚出现不久的 CRT 彩色电视定制一套标准,由于实在是太过于古老
72%NTSC:100%的sRGB色域约等于72%的NTSC色域
100%sRGB/72%NTSC 以上色域的屏幕,是不错的屏幕
90%AdobeRGB/90%NTSC 以上的屏幕,是非常优秀的屏幕。
尼特是亮度的单位,1nit=1 cd/m²
亮度的单位是坎德拉/平方米(cd/m2)亮度是人对光的强度的感受。
A “nit” is another way to describe a brightness of 1 candela per square meter (cd/m2). An average candle produces roughly 1 candela.
lumens typically only apply to projectors. It tells you how much light energy something is throwing out, but not exactly how “bright” it will appear. That’s because you’re not looking directly at a projector. If a projector has “2,000 lumens” for example, it’s going to appear differently bright whether you use a 50-inch screen or a 150-inch screen.
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the derived SI unit of luminance. The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”
TüV标志是德国TüV专为元器件产品定制的一个安全认证标志,在德国和欧洲得到广泛的接受。
应用安全标准的目的是:防止家电产品、机械产品、汽车产品使用过程中可能产生的各种危险所造成的人身伤害和财产损失。
包括电击或触电,温度过高或火灾,机械方面存在的危险,放射性危险,化学性危险。
USB-PD 是由 USB-IF 组织制定的一种快速充电规范,是目前主流的快充协议之一。 USB-PD 快充协议是以 Type-C 接口输出的,但不能说有 Type-C 接口就一定支持 USB-PD 协议快充
PD快充协议是什么 PD的全名应该叫做USB Power Delivery Specification,是USB的标准化组织推出的一个快速充电的标准。USB PD 3.0的协议理论上需要USB 3.0的接口
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a publicly available specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware
规模以上工业企业,即年主营业务收入为2000万元及以上的工业法人单位。
Quantitative easing (QE) is a form of unconventional monetary policy in which a central bank purchases longer-term securities from the open market in order to increase the money supply and encourage lending and investment.
CNAS认可,为中国合格评定国家认可委员会(China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment,CNAS)的认证英文缩写,是在原中国认证机构国家认可委员会(CNAB)和中国实验室国家认可委员会(CNAL)基础上合并重组而成的。
1.国际认可论坛(IAF)互认
2.国际实验室认可合作组织(ILAC)实验合作组织互认
3.中国CNAS认证与区域组织互认:
4.与太平洋认可合作组织(PAC)互认
5.与亚太实验室认可合作组织(APLAC)互认
EMI(Electro Magnetic Interference)直译是“电磁干扰”,是指电子设备(干扰源)通过电磁波对其他电子设备产生干扰的现象。
有矛就有盾,有电磁干扰就有抗电磁干扰。下面请出我们的第二位主角EMS。EMS(Electro Magnetic Susceptibility)直译是“电磁敏感度”,是指由于电子设备受到外界的电磁能量,造成自身性能下降的容易程度。
EMC(Electro Magnetic Compatibility)直译是“电磁兼容性”,是指电子设备所产生的电磁能量既不对其他电子设备产生干扰,也不受其他电子设备的电磁能量干扰的能力
An alternative to Quantum Dots, phosphor-coated LEDs have a chemical coating to alter the light’s output.\
oled
This stands for organic light-emitting diode. In an OLED display, the pixels also produce their own light, eliminating the need for an additional LED backlight, making OLED screens super thin. Because each pixel can be individually turned off when not in use, OLED displays create a perfect black, which is why you will see claims of “infinite contrast” on some OLED models.
Today most monitors that use LCD technology are backlit with LEDs, so typically if you’re buying a monitor it’s both an LCD and LED display.
液晶显示器的常用面板有TN(Twisted Nematic扭曲向列型)、IPS(In-Plane-Switching平面转换型)、VA(Vertical Alignment多象限垂直配向型)三种类型,前两种相对常见。
TN屏就是较早前常见的软屏,用手能按出水波纹,这是较早使用的LCD面板之一,目前也在大量使用,因为它的技术成熟,成本低。TN屏响应速度快,可以达到1ms的响应时间,不会出现残影。使用这种材质的屏幕通常用来作为职业电竞屏,通过快速响应,TN屏可无损呈现高速变化的场景细节。
缺陷也很明显,输出灰阶少,原生只有6bit色彩,画面色彩偏白、可视角度小,显示效果一般,通过不同角度观看会出现偏色和亮度差别。因此,如果你从事设计、影视后期相关工作或在观影娱乐时对屏幕色彩有较高要求,不建议使用这种屏幕。
IPS屏面板较硬,用手指轻触屏幕,画面不会变形。IPS屏在色彩显示、可视角度等方面比TN面板好上不少,对于色彩的呈现范围与准确性也都有亮眼的表现,广视角是IPS面板的原生优势,不论哪个角度观看都不会产生色偏。目前跟影像处理有关的专业屏幕大多采用IPS面板。
为了改良推出了Nano-IPS、Fast-IPS面板,响应时间有了大提升,不少搭配这两种面板的显示器达到了1ms(GTG)
响应时间超级高的Fast IPS显然更好一些。而想两者兼备的话就选择NanoIPS面板
灰阶响应时间 [1] ,也就是GTG(Grey To Grey)。说到灰阶响应时间,首先来看一下什么是灰阶。我们看到液晶屏幕上的每一个点,即一个像素,它都是由红、绿、蓝(RGB)三个子像素组成的,要实现画面色彩的变化,就必须对RGB三个子像素分别做出不同的明暗度的控制,以“调配”出不同的色彩。这中间明暗度的层次越多,所能够呈现的画面效果也就越细腻。以8 bit的面板为例,它能表现出256个亮度层次(2的8次方),我们就称之为256灰阶。
MPRT全拼是Moving Picture Response Time,翻译过来叫“动态画面响应时间”,MPRT只是一种降低画面模糊的技术手段,
国际照明委员会(英语:International Commission on illumination,法语:Commission Internationale de l´Eclairage,采用法语简称为CIE [1] )是由国际照明工程领域中光源制造、照明设计和光辐射计量测试机构组成的非政府间多学科的世界性学术组织,是技术、科学、文化方面的非营利组织。
VESA方案主要与显示器的最大峰值亮度能力相关联,每个数字代表背光最大亮度规格。例如,VESA DisplayHDR 400适用于可达到400 cd / m2峰值亮度的屏幕
视频电子标准协会(Video Electronics Standards Association, VESA)是由代表来自世界各地的、享有投票权利的140多家成员公司的董事会领导的非盈利国际组织
DisplayPort:显示设备端口,是数字显示设备图像和声音接口的标准化格式。
通过此HDR 400认证将屏幕标记为支持HDR,这是毫无意义和误导我们的感受
BC1.2 (Battery Charging v1.2)是USB-IF下属的BC(Battery Charging)小组制定的协议,主要用于规范电池充电的需求,该协议最早基于USB2.0协议来实现。
BC1.2引入了充电端口识别机制,主要包括以下几个USB端口类型:
1.标准下行端口(SDP)
SDP端口支持USB协议,最大电流500mA,可以认为SDP就是普通的USB接口
2.专用充电端口(DCP)
DCP不支持数据协议,支持快充,可以提供大电流,DCP主要用于墙充等专用充电器
3.充电下行端口(CDP)
CDP既支持数据协议也支持快充
USB-IF组织推出PD协议(Power Delivery 功率传输协议),有望统一快充市场。
Color accuracy
ΔE(Delta-E),指的是在均匀颜色感觉空间中,人眼感觉色差的测试单位·这种测试方法用于当用户指定或接受某种颜色时,生产商用以保证色彩一致性的量度·。
ΔE值在1.6到之间3.2,人眼基本上是分辨不出色彩的差异,这里只有少数专业级显示器,
在6.5到13之间时,色彩差别已经可以判别,但色调本身仍然相同。此时市面上大多数消费级液晶显示器都在这个档次上;
HDCP(High -bandwidth Digital Content Protection):高带宽数字内容保护技术。
HDCP协议是用来防止视频内容在传输的过程被完整的复制下来
接口
高清多媒体接口(High Definition Multimedia Interface,HDMI [1] )是一种全数字化视频和声音发送接口,可以发送未压缩的音频及视频信号。
HDMI 1.4标准兼容的功能都应支持ARC
HDMI 2.1还提供了新的和改进的ARC版本,称为增强音频回传通道(eARC)将支持杜比全景声(Dolby Atmos)和其他未压缩的声音格式。
It offers new enhancements for video games like variable refresh rate (VRR) and automatic low-latency mode (ALLM) and the ability to pass 4K signals to the TV at up to 120Hz, for ultra-smooth motion.
HEVC (H.265)
Stands for “High-Efficiency Video Coding.” A new compression technology developed to make large 4K UHD video files smaller and, therefore, easier to stream over broadband Internet connections. HEVC is said to double the data compression ratio over H.264, the predominant encoding technology used today for 1080p videos while retaining the same video quality. A smart TV or streaming set-top box must be able to decode HEVC to playback 4K Ultra HD video
D65光源是标准光源中最常用的人工日光,其色温为6500K。英文名:Artificial Daylight 6500K。标准光源箱中的D65光源是模拟人工日光,保证在室内、阴雨天观测物品的颜色效果时,有一个近似在太阳光底下观测的照明效果。
基本科学指标数据库(Essential Science Indicators,简称ESI)是由世界著名的学术信息出版机构美国科技信息研究所(ISI)于2001年推出的衡量科学研究绩效、跟踪科学发展趋势的基本分析评价工具。
AUX接口(Auxiliary)是指音频输入接口,可以输入包括mp3在内的电子声频设备的音频(一般的耳机插孔),可通过车上的音响来输出这些设备内的音乐。
DTS [1] 成立于1993年,总部设于美国加州Calabasas
从最初声名卓著的多声道音频技术先锋,到DTS发展为蓝光的必备音频标准之一。并在电影数字传输和与其他各种互联网相关的消费电子平台上获得了广泛的应用
Digital Theater System
DTS-HD Master Audio (DTS-HD MA; known as DTS++ before 2004[1]) is a multi-channel, lossless audio codec developed by DTS as an extension of the lossy DTS Coherent Acoustics codec (DTS CA; usually itself referred to as just DTS).DTS-HD Master Audio (DTS-HD MA; known as DTS++ before 2004[1]) is a multi-channel, lossless audio codec developed by DTS as an extension of the lossy DTS Coherent Acoustics codec (DTS CA; usually itself referred to as just DTS).
S/PDIF的全称是Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format,是索尼与飞利浦公司合作开发的一种民用数字音频接口协议
antenna这个单词词语,这个单词其实是天线意思,所以它的对应接口实际上就是天线接口,是专门用来接天线的端口。
AV接口实现了音频和视频的分离传输,在成像方面可以避免音频与视频互相干扰而导致的画质下降。AV接口在电视与DVD连接中使用的比较广,是每台电视必备的接口之一
音频、视频分离的视频接口,一般由三个独立RCA插头组成,其中V接口连接混合视频信号,为黄色插口;L接口连接左声道声音信号,为白色插口;R接口连接右声道声音信号,为红色插口。
AV接口,音频(Audio )和视频(Video )的简称.
AV端口(又称复合端口)原文为Composite video connecto
美国无线电公司(Radio Corporation of America,RCA)在1930年代的大多收音机中采用了这样的连接方式,也正是这种接头得名的原因。
RCA端子(RCA jack,或RCA connector),俗称梅花头、莲花头,是一种应用广泛的端子,可以应用的场合包括了模拟视频/音频(例:AV端子(三色线))、数字音频(例:S/PDIF)与色差分量(例:色差端子)传输等。
UPS即不间断电源(Uninterruptible Power Supply),是一种含有储能装置的不间断电源。主要用于给部分对电源稳定性要求较高的设备,提供不间断的电源。当市电输入正常时,UPS 将市电稳压后供应给负载使用,此时的UPS就是一台交流式电稳压器,同时它还向机内电池充电;当市电中断(事故停电)时, UPS 立即将电池的直流电能,通过逆变器切换转换的方法向负载继续供应220V交流电,使负载维持正常工作并保护负载软、硬件不受损坏。UPS 设备通常对电压过高或电压过低都能提供保护。
Thunderbolt技术融合PCI Express和DisplayPort两种通信协议。其中PCI Express用于数据传输,可以非常方便的进行任何类型设备扩展;DisplayPort用于显示,能同步传输1080p乃至超高清视频和最多八声道音频。并且两条通道在传输时都有自己单独的通道,不会产生任何干扰。
雷电接口物理外观多为Type-C接口。。Thunderbolt使用铜质线缆,长度限制为3米。
DisplayPort(简称DP)是一个由PC及芯片制造商联盟开发,视频电子标准协会(VESA)标准化的数字式视频接口标准。此接口的设计是为取代传统的VGA、DVI和FPD-Link(LVDS)接口。
Speaker and Sound card
other input/output devices
keyboard
mouse
microphone
webcam
半导体
A logic gate is an idealized model of computation or physical electronic device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output.
数字集成电路按导电类型可分为双极型集成电路(主要为TTL)和单极型集成电路(CMOS、NMOS、PMOS等)
PMOS logicNMOS logic
CMOS是Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor(互补金属氧化物半导体)的缩写。它是指制造大规模集成电路芯片用的一种技术或用这种技术制造出来的芯片,是电脑主板上的一块可读写的RAM芯片。因为可读写的特性,所以在电脑主板上用来保存BIOS设置完电脑硬件参数后的数据,这个芯片仅仅是用来存放数据的。
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced “see-moss”), also known as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (COS-MOS), is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions.
CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first “transistor”) and the amplifying function (the second “transistor”), as opposed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) or diode–transistor logic (DTL).
Resistor–transistor logic (RTL) (sometimes also transistor–resistor logic (TRL)) is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices.
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
Diode–transistor logic (DTL) is a class of digital circuits that is the direct ancestor of transistor–transistor logic. It is called so because the logic gating function (e.g., AND) is performed by a diode network and the amplifying function is performed by a transistor (in contrast with RTL and TTL).
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
行业
多晶硅的需求主要来自于半导体和太阳能电池
polycrystalline silicon
多晶硅,是单质硅的一种形态。熔融的单质硅在过冷条件下凝固时,硅原子以金刚石晶格形态排列成许多晶核,如这些晶核长成晶面取向不同的晶粒,则这些晶粒结合起来,就结晶成多晶硅。
tsmc台湾积体电路制造股份有限公司Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company
manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP)
锦标,本是锦制的标旗,后泛指授给竞赛优胜者的奖品。锦标赛(Championships/ Tournament)指不同地区或竞赛大组的优胜者之间的一系列决赛之一。锦标赛是排名在一定水平上的人才可以参加,而且每个国家的选手数量限制。
over-the-air (OTA)
The conference therefore established the Greenwich Meridian as the prime meridian and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as the world’s time standard.
UTC is one of several closely related successors to GMT.
2002年的电子政府法案(E-Government Act)包含联邦信息安全管理法案(Federal Information Security Management Act,FISMA)。FISMA要求政府机构和部门要设置信息管理和信息系统的基本安全目标来提高安全性,强制实行了联邦信息处理标准(Federal Information Processing Standard,FIPS)。
Definition of ‘aka’
a. is an abbreviation for ‘also known as. ‘ a.k.a. is used especially when referring to someone’s nickname or stage name.
半导体产业中有两大分支:集成电路和分立器件。Discrete device
芯片设计企业(Fabless)、晶圆代工厂(Foundry)、封测厂(OSAT)完成,形成产业链协同效应。
IDM(Integrated Design and Manufacture)垂直整合制造 ,指从设计、制造、封装测试到销售自有品牌IC都一手包办的半导体垂直整合型公司。
Fabless,是Fabrication(制造)和less(无、没有)的组合,是指“没有制造业务、只专注于设计”的集成电路设计的一种运作模式,也用来指代未拥有芯片制造工厂的IC设计公司,经常被简称为“无晶圆厂”(晶圆是芯片\硅集成电路的基础,无晶圆即代表无芯片制造);通常说的IC design house(IC设计公司)即为Fabless。
Foundry,在集成电路领域是指专门负责生产、制造芯片的厂家。Foundry原意为铸造工厂、翻砂车间、玻璃熔铸车间,从它的字面意思可以看出其与集成电路的联系,因为硅集成电路的制造也跟“玻璃”和“砂”有关。
OEM(Original Equipment Manufacturer,指的是品牌、设计、销售一方和生产一方进行合作的模式,俗称“代工”、“贴牌”;
而ODM(Original Design Manufacturer)则是生产制造商,除了担任制造这个主要责任外,还有部分是自己设计的。
介于两者之间的Fablite模式,即“轻晶圆”模式
OSAT,全称为Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing,字面意思就是「外包半导体(产品)封装和测试」,是为一些Foundry公司做IC产品封装和测试的产业链环节。
MOS memory MPU / MCU Analog Logic ASIC ASSP
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC /ˈeɪsɪk/) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use.
An application-specific standard product or ASSP is an integrated circuit that implements a specific function that appeals to a wide market. As opposed to ASICs that combine a collection of functions and are designed by or for one customer, ASSPs are available as off-the-shelf components. ASSPs are used in all industries, from automotive to communications.
mpu A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits.
mcu A microcontroller (MCU for microcontroller unit) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals.
DSP 数字信号处理器
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip.
SoC:System on Chip的缩写,称为系统级芯片,也有称片上系统,意指它是一个产品,是一个有专用目标的集成电路,其中包含完整系统并有嵌入软件的全部内容。
复合增长率来衡量,由于它是长期时间基础上的核算,所以更能够说明产业或产品增长或变迁的潜力和预期。
复合年均增长率,简称CAGR(Compound Annual Growth Rate)。是一项投资在特定时期内的年度增长率。
半导体产品包括集成电路、光电器件、分立器件、传感器四大类
光电器件(Optoelectronics)包括半导体显示、半导体灯、光耦合器、光开关、图像传感器和其他光感应和发射半导体器件等
传感器/执行器(Sensors & Actuators)指电学特性被设计成与温度、压力、位移、速度、加速度、应力、应变或任何其他物理、化学或生物特性相关的半导体器件,包括温度传感器、压力传感器、磁场传感器、执行器等。所有光学传感器归类于光电子类别。
分立器件(Discretes)包括二极管、小信号和开关晶体管、功率晶体管、整流器、晶闸管等。
晶闸管Thyristor具有硅整流器件的特性,能在高电压、大电流条件下工作,
半导体行业包括设计、制造、封测三个环节。
也称晶圆制造:半导体制造环节指由晶圆制造厂完成的前道工艺,包括氧化/扩散、光刻、刻蚀、离子注入、薄膜生长、清洗与抛光、金属化等七大工艺步骤
薄膜生长、刻蚀和光刻设备为晶圆制造核心设备,其市场规模最大
半导体硅片是最重要的晶圆制造材料,
封测环节指由封测厂完成的后道工艺,包括贴膜、磨片、贴片、划片、装片、键合、测试等
2022 年二季度全球前十大晶圆代工厂的合计市占率达98%,其中台积电稳居全球第一,市占率为 53.4%;排名第二的三星市占率为 16.5%;其他厂商市占率均为个位数。
IP(Intellectual Property)是指集成电路设计中预先设计、验证好的功能模块,通常由第三方 IP 供应商开发,并提供成熟的IP 模块给芯片设计公司用于集成,可有效缩短芯片设计周期并提升芯片性能。当前国际上绝大部分SoC都是基于多种不同 IP 组合进行设计的
IP 核分为软核、硬核和固核三种。按照开发完成度,IP 核可划分为软核、固核、硬核三类,软核一般指使用硬件描述语言(HDL)形式提供给客户的代码文件,其中不涉及具体电路元件实现等功能,软核代码直接参与设计的编译流程,以HDL代码形式呈现;固核设计程度介于软核与硬核之间,用户可以根据需求重新定义性能参数,内部连线表可根据需求进行优化,最终以HDL 门级电路网表呈现;硬核是设计阶段最终产品,提供给用户光掩模图和全套工艺文件。从完成IP核所花费的成本来讲,硬核代价最大;从使用灵活性来讲,软核最高。
CPU IP 占比 36.0%,DSP IP 占比 5.1%,GPU/ISP IP 占5.1%,接口IP 占比 22.1%,其他合计占比 26.9%。
ISP(Image Signal Processing) 图像信号处理。主要用来对前端图像传感器输出信号处理的单元,以匹配不同厂商的图像传感器。
摩尔定律由英特尔创始人之一戈登·摩尔在 1965 年提出,是指集成电路上可以容纳的晶体管数目在大约每经过 18 个月到 24 个月便会增加一倍。
逻辑制程CMOS 严格按照摩尔定律推进
半导体工艺主要包括 BJT、PMOS、NMOS、CMOS、BiCMOS、BCD、HV-CMOS 等。
BJT 工艺(Bipolar Junction Transistor,双极型晶体管)
PMOS 工艺(Positive channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor,P 沟道金属氧化物半导体)
NMOS 工艺(Negative channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor,N 沟道金属氧化物半导体)
CMOS 工艺(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor,互补金属氧化物半导体):CMOS 是将 NMOS 和 PMOS 制造在同一个芯片上,利用互补对称电路来配置连接 PMOS 和 NMOS 从而形成逻辑电路,静态功耗理论上接近零。CMOS 工艺成为超大规模集成电路的主流工艺。
BiCMOS 工艺将双极型和CMOS 器件制造在同一个芯片上。主要用于 RF 电路、LED 控制驱动和 IGBT 控制驱动;
IGBT(Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor),绝缘栅双极型晶体管,是由(Bipolar Junction Transistor,BJT)双极型三极管和绝缘栅型场效应管(Metal Oxide Semiconductor,MOS)组成的复合全控型电压驱动式功率半导体器件。非常适合应用于直流电压为600V及以上的变流系统
“RF 是Radio Frequency的缩写,表示可以辐射到空间的电磁频率,频率范围从300KHz~30GHz之间。
射频简称RF”
BCD 工艺将双极型、CMOS 和 DMOS(扩散 MOS)器件制作在同一芯片上。DMOS 器件可以耐高压,适合高压功率部分。BCD 工艺主要用于电压管理、显示驱动等;
HV-CMOS 将高压 MOS 和 CMOS 制作在同一芯片上,高压MOS器件可以承受高压,但电流驱动能力较弱,成本低于BCD 工艺,适合只需要驱动高压信号,而没有大功率要求的芯片,主要用于 ACDC、DCDC、高压数模混合电路、LCD 和 LED 屏幕驱动等。
在制程进入20nm 以下时,原有的Planar FET(平面场效应晶体管,一面有栅极)面临漏电和栅极对通道控制不足等问题,为了继续提高集成度,FinFET(鳍式场效应晶体管,三面有栅极)和GAAFET(全栅场效应晶体管,四面有栅极)被研发出来。
TV Programming rated
Although TV-14 is technically for ages 14 and up, Netflix’s notice implies 15 instead, as it states “Parents Strongly Cautioned. May not be suitable for ages 14 and under.”
D: Intensely Suggestive Dialogue
L: Strong Coarse Language
S: Intense Sexual Content
V: Intense Violence
Programming rated TV-PG as stated in the United States TV Parental Guidelines signifies content with parental guidance suggested
D: Mildly Suggestive Dialogue
L: Infrequent Coarse Language
S: Mild Sexual Content
V: Mild Violence
TV-Y icon.svg TV-Y – This program is aimed at a very young audience, including children from ages 2–6.[67]
TV-Y7 icon.svg TV-Y7 – This program is designed for children age 7 and above.[67]
TV-Y7-FV icon.svg Some programs may be given the “FV” content descriptor if they exhibit more ‘fantasy violence’ that may be more intense or combative than other programs rated TV-Y7.[67]
TV-G icon.svg TV-G – Most parents would find this program suitable for all ages.[67] Programs rated TV-G are generally suitable for all ages. The FCC states that “this rating does not signify a program designed specifically for children, most parents may let younger children watch this program unattended.”[67] The thematic elements portrayed in programs with this rating contain little or no violence, no strong language, and little or no sexual dialogue or situations.[68]
TV-PG icon.svg TV-PG – Parental guidance is recommended; these programs may be unsuitable for younger children.[67]
TV-14 icon.svg TV-14 – This program contains some material that many parents would find unsuitable for children under 14 years of age.[67]
TV-MA icon.svg TV-MA – This program is intended to be viewed by adults and therefore may be unsuitable for children under 17.[67]
pay television
Thematic material is rated based on a ten-code system, designated with a two- or three-letter abbreviation and corresponding descriptor:
AC – Adult Content
AL – Adult Language
GL – Graphic Language (exclusive to R/TV-MA-rated programs)
MV – Mild Violence
V – Violence
GV – Graphic Violence
BN – Brief Nudity
N – Nudity
SSC – Strong Sexual Content (exclusive to R/TV-MA-rated programs)
RP – Rape
Irl is an abbreviation for the phrase in real life. Use irl when you want to distinguish reality from something that happens in games, on social media, or on TV.
game
A massively multiplayer online game (MMOG, or more commonly, MMO) is an online game with large numbers of players, often hundreds or thousands, on the same server.
A MUD (/mʌd/; originally multi-user dungeon, with later variants multi-user dimension and multi-user domain)通常将缩写字直译为“网络泥巴”或是简称“泥巴”(英文 mud 的意思为泥巴)。是一款多人即时的虚拟世界,通常以文字描述为基础。 MUD 结合了角色扮演、砍杀、玩家与玩家对战、互动小说与在线聊天等元素,玩家可以阅读或查看房间、物品、其他玩家、非玩家角色的描述,并在虚拟世界中做特定动作。 玩家通常会通过输入类似自然语言的指令来与虚拟世界中的其他玩家互动。
Third-person shooter (TPS) is a subgenre of 3D shooter games in which the gameplay consists primarily of shooting. It is closely related to first-person shooters, but with the player character visible on-screen during play. While 2D shoot ‘em up games also employ a third-person perspective, the TPS genre is distinguished by having the game presented with the player’s avatar as a primary focus of the camera’s view.
An arcade game or coin-op game is a coin-operated entertainment machine typically installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars and amusement arcades.
2.5D (two-and-a-half dimensional, alternatively pseudo-3D or three-quarter) perspective
Windows Display Driver Model WDDM is the graphic driver architecture for video card drivers running Microsoft Windows versions beginning with Windows Vista.
A system on a chip (SoC; /ˌɛsˌoʊˈsiː/ es-oh-SEE or /sɒk/ sock[nb 1]) is an integrated circuit (also known as a “chip”) that integrates all or most components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output ports and secondary storage, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip
Virtual reality (VR) is an interactive, computer-generated depiction of a real or artificial world or activity. Mixed reality (MR) is an interactive depiction or view of combined real-world and computer-generated elements. Augmented reality (AR) is a real-world view with additional, computer-generated enhancements.
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR)
eXtended Reality (XR) is a ‘catch-all’ term for technologies that enhance or replace our view of the world.
a key fact, point, or idea to be remembered, typically one emerging from a discussion or meeting.
Estimated Time of Arrival
尤其用于军方,作为军事用语,如,ETA 3 minutes,其意思就是预计三分钟之后到达。
耐受性(Tolerance)是指人体对药物反应性降低的一种状态,按其性质有先天性和后天获得性之分。耐受性是一种生物学现象,是药物应用的自然结果。.
策略角色扮演游戏(Strategy Role-Playing Game)的,简称SRPG。是一种在日本十分流行的、带有战术性的(通常为战棋类)的角色扮演游戏。在日本,被称为“模拟角色扮演”(シミュレーションRPG),在美国被称为战术角色扮演(Tactical role-playing game)。因为“模拟角色扮演”(即策略角色扮演,Simulation RPG)和“角色扮演模拟游戏”(Role-playing Simulation)很容易混淆,所以不建议使用这种称呼。
Life simulation games form a subgenre of simulation video games in which the player lives or controls one or more virtual characters (human or otherwise). Such a game can revolve around “individuals and relationships, or it could be a simulation of an ecosystem”.[1] Other terms include artificial life game[1] and simulated life game (SLG).
SLG=Simulation Game,策略类游戏。现特指回合制策略游戏以及即时SLG。有别于SIM(Simulation)类“生活“模拟游戏,SLG虽然也是缩写的simulation(模拟但与经营类意思不同),却是“战争策略“模拟游戏的总称。
模拟经营游戏,是电子游戏类型的一种,由玩家扮演管理者的角色,对游戏中虚拟的现实世界进行经营管理。
ACG即日本动画(Anime)、漫画(Comics)与电子游戏(Games)
“TVB Superchannel”, tvbs
tvb Television Broadcasts Limited (TVB) is a television broadcasting company based in Hong Kong.
智能硬件
3C 指 计算机、通讯、消费电子产品
FWA 指 Fixed Wireless Access,即固定无线接入
OTT 指 Over-The-Top,即互联网机顶盒
“Original Design Manufacturer,即自主设计制造,指结构、外观、
工艺等主要由生产商自主开发,产品以客户的品牌进行销售的一种
运营模式”
ict Information and communications technology
智能硬件指的是具备联网、感知、交互、推理学习能力的硬件产品。
Low-power wide-area networking (LPWAN) – Wireless networks designed to allow long-range communication at a low data rate, reducing power and cost for transmission. Available LPWAN technologies and protocols: LoRaWan, Sigfox, NB-IoT, Weightless, RPMA.
LTE Cat NB1 26 kbit/s
Narrowband Internet of things (NB-IoT) is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) radio technology standard developed by 3GPP for cellular devices and services
LTE Cat M1 1 Mbit/s
LTE-M or LTE-MTC (“Long-Term Evolution Machine Type Communication”), is a type of low-power wide-area network radio communication technology standard developed by 3GPP for machine-to-machine and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
LTE Cat 1 10 Mbit/s
微机电系统Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems)
TWS的全称是True Wireless Stereo,意思是真正无线立体声。TWS技术是基于蓝牙芯片技术发展而来的。
蓝牙耳机左右是连在一起的,现在则左右成了两只,成了“真无线”
osd是on screen display的简称,是屏幕菜单式调节方式。2、通过屏幕来调节显示器的各项信息的矩形菜单
显示面板驱动IC(DDIC)
车机
车机指的是安装在汽车里面的车载信息娱乐产品的简称,车机在功能上能够实现人与车,车与外界(车与车)的信息通讯。
A human interface device or HID is a type of computer device usually used by humans that takes input from humans and gives output to humans.
Since HID’s original definition over USB, HID is now also used in other computer communication buses. This enables HID devices that traditionally were only found on USB to also be used on alternative buses. This is done since existing support for USB HID devices can typically be adapted much faster than having to invent an entirely new protocol to support mouse, touchpad, keyboards, and the like. Known buses that use HID are:
Bluetooth HID – Used for mouse and keyboards that are connected via Bluetooth
数字信号处理
Digital Signal Process
智能锁
市场中锁芯的等级按照国家标准来判定可以分为a级、b级和超b级,其中指纹锁绝大部分使用b级和超b级,而业内将超b级称之为c级。
指静脉识别是静脉识别的一种,首先通过指静脉识别仪取得个人手指静脉分布图,从手指静脉分布图依据专用比对算法提取特征值,通过近红外光线照射,利用CCD摄像头获取手指静脉的图像,将手指静脉的数字图像存贮在计算机系统中,将特征值存储。实际上它和初代指纹识别的方式比较接近,依靠的是图像特征比对来进行认证和识别。
coupled
linked or connected in a pair or pairs.
CCD感光元件,英文全称:Charge-coupled Device,中文全称:电荷耦合元件。可以称为CCD图像传感器。CCD是一种半导体器件,能够把光学影像转化为数字信号。
光学指纹头(来自度娘)
借助光学技术采集指纹是历史最久远、使用最广泛的技术。将手指放在光学镜片上,手指在内置光源照射下,用棱镜将其投射在CCD(电荷耦合器件)上,进而形成脊线(指纹图像中具有一定宽度和走向的纹线)呈黑色、谷线(纹线之间的凹陷部分)呈白色的数字化的、可被指纹设备算法处理的多灰度指纹图象。
半导体手续费头(来自度娘)
无论是电容式还是电感式,其原理类似,在一块成千上万半导体器件的“平板”上,手指贴在其上与其构成了电容(电感)的另一面,由于手指平面凸凹不平,凸点处和凹点处接触平板的实际距离大小就不一样,形成了电容(电感)数值就不一样,设备根据这个原理将采集到的不同的数值汇总,就完成了指纹采集。
半导体指纹识别模块只是、识别活体指纹,安全性高,也就是说半导体指纹头可穿透皮肤表发层,所以网上盛传的硅胶模拟指纹在这里基本上起不了什么作用,识别活体指纹锁的好处在于指纹基本上不能被复制或者仿制。
半导体指纹识别模块不易保养,半导体指纹头的采集窗口会受到污渍汗渍以及静电的影响,容易被划花,所以需要使用时注意保护和养护,不然使用寿命难以保障
相对湿度(Relative Humidity ),用RH表示。表示空气中的绝对湿度与同温度和气压下的饱和绝对湿度的比值,得数是一个百分比。
LR6电池特色是适用于大电流用电器具,如电动玩具、照相机闪光灯、剃须刀等,使用时间较长;而R6P电池虽也可用于上述这些用电器,但使用时间仅为LR6电池的1/3。从价格上看,R6P电池零售价约1元/只,LR6电池2~3元/只
Chemistry IEC name
Zinc–carbon R6
Alkaline LR6
The International Electrotechnical Commission[3] (IEC; in French: Commission électrotechnique internationale) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as “electrotechnology”.电气、电子
电工
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈrɛindaːl]), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001
Cryptography密码学
过滤器
总溶解固体(英文:Total dissolved solids,缩写TDS),又称溶解性固体总量,测量单位为毫克/升(mg/L),它表明1升水中溶有多少毫克溶解性固体。由于天然水中所含的有机物以及呈分子状的无机物一般可以不考虑,所以一般也把含盐量称为总溶解固体。
reverse osmosis反渗透又称逆渗透,是一种以压力差为推动力,从溶液中分离出溶剂的膜分离操作。对膜一侧的料液施加压力,当压力超过它的渗透压时,溶剂会逆着自然渗透的方向作反向渗透。从而在膜的低压侧得到透过的溶剂,即渗透液;高压侧得到浓缩的溶液,即浓缩液。
PPI
DPI(Dots Per Inch,每英寸点数)是一个量度单位
DPI是打印机、鼠标等设备分辨率的度量单位。是衡量打印机打印精度的主要参数之一,一般来说,DPI值越高,表明打印机的打印精度越高。
PPI(pixels per inch)